Approaches to E-Waste, Battery Waste Disposal in Healthcare Facilities
Read the Magazine in PDF
Abstract
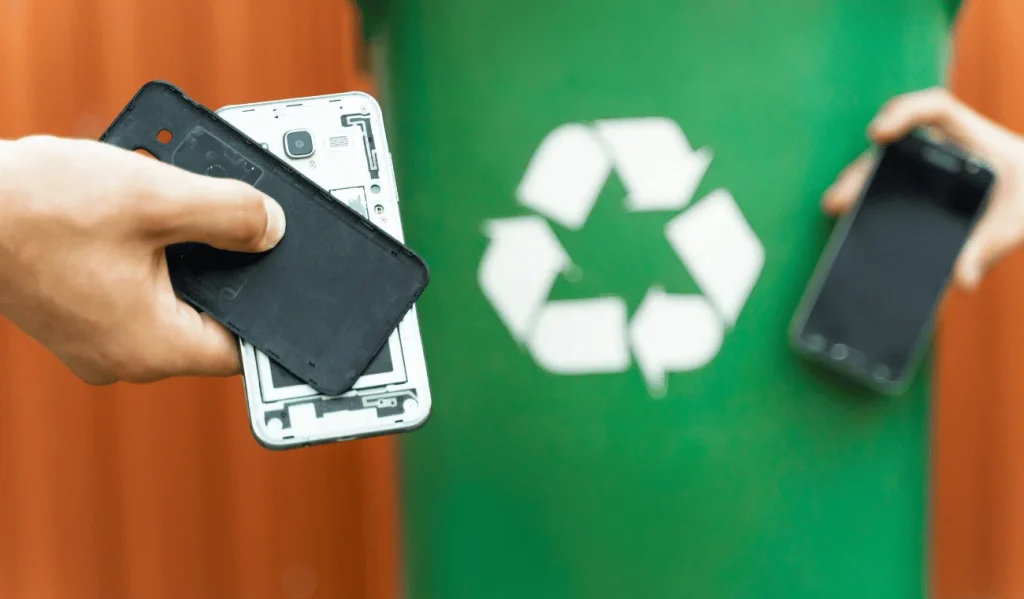
Healthcare facilities are prolific generators of electronic waste (e-waste) and battery waste, posing environmental and health risks due to hazardous components like lead, mercury, and cadmium. Disposal mismanagement of these wastes can result in severe consequences, including environmental contamination and adverse health effects. This article delineates strategies for proper e-waste and battery waste management in healthcare settings, emphasizing the need for responsible disposal practices to mitigate environmental impact and safeguard public health.
Introduction
Healthcare facilities are major generators of electronic waste (e-waste) and battery waste, due to the extensive use of medical equipment, diagnostic devices, and power tools. Improper disposal of these wastes can pose significant environmental and health risks, as they contain hazardous substances such as lead, mercury, and cadmium. Therefore, it is crucial for healthcare facilities to implement proper strategies for managing and disposing of e-waste and battery waste in an environmentally responsible and safe manner.
E- Waste Management
E-waste encompasses a wide range of electronic products, including computers, monitors, printers, scanners, medical equipment, and batteries. Improper disposal of e-waste can lead to the release of toxic chemicals into the environment, contaminating soil, water, and air. These pollutants can harm human health, causing respiratory problems, neurological disorders, and even cancer.
To effectively manage e-waste in healthcare facilities, the following strategies can be implemented:
- Establish a dedicated e-waste collection program: Designate specific containers or bins for the collection of e-waste, ensuring they are clearly labelled and located in accessible areas.
- Reduce e-waste generation: Encourage the use of eco-friendly alternatives, extend the lifespan of equipment through proper maintenance, and consider leasing or renting equipment instead of purchasing.
- Segregate waste streams: Separate e-waste from other waste streams, such as regular trash or hazardous waste, to minimize contamination risks.
- Conduct audits and inventory management: Regularly conduct audits to track e-waste generation and identify areas for improvement in waste reduction and management practices.
- Source separation and recycling: Collaborate with certified e-waste recyclers who follow strict environmental and safety guidelines. Require recyclers to provide documentation of proper disposal practices.
- Community involvement: Engage with local recycling organizations and participate in community e-waste collection events to expand the reach of waste management efforts.
Battery Waste Management: Batteries contain valuable metals such as lithium, cobalt, and nickel, but they also pose environmental and health risks due to the presence of hazardous materials like lead, cadmium, and mercury. Improper disposal of batteries can lead to fires, explosions, and the leaching of toxic chemicals into the environment.
Strategies for Battery Waste Management in Healthcare Facilities: To manage battery waste effectively, consider the following strategies:
- Set aside particular containers for collecting batteries: Provide easily accessible, clearly labelled containers for gathering several kinds of batteries, including rechargeable, lithium-ion, and alkaline batteries.
- Assist initiatives that recycle batteries: Work together with authorized recyclers of batteries that are experts in handling and processing different kinds of batteries securely.
- Encourage the use of reusable batteries: Promote the longer usage of rechargeable batteries before their disposal.
- Provide battery swapping initiatives: To reduce the amount of used batteries that accumulate, implement initiatives that encourage the exchange of old batteries for new rechargeable ones.
Regulation Compliance: When it comes to the handling of battery waste and e-waste, healthcare institutions need to follow all applicable local, state, and national rules. By guaranteeing that these hazardous wastes are handled, recycled, and disposed of properly, these rules seek to safeguard both the environment and human health. For effective disposal of this waste refer to the policy published by the Government of India under the Ministry of Environment, Forest, and Climate Change. The forms that need to be submitted to the Pollution Control Board (PCB) concerning e-waste and battery waste are as follows:
For e-waste:
- Form 1 (a): Application for authorization to collect, transport, process, or recycle e-waste
- Form 4: Application for authorization to dismantle e-waste
- Form 6: Application for authorization to incinerate e-waste
- Form 7: Application for authorization to import e-waste
- Form 8: Application for authorization to handle e-waste as hazardous waste
For battery waste:
- Implement battery safety protocols: Provide clear guidelines for the safe handling, storage, and disposal of batteries, especially those containing hazardous substances.
- Schedule I: Report on the generation, collection, and disposal of battery waste
- Schedule II: Report on the storage and transportation of battery waste
- Schedule III: Report on the management of hazardous substances in battery waste
- Schedule IV: Report on the disposal of hazardous substances in battery waste
- Schedule V: Report on the compliance with the Battery Waste Management Rules, 2022
In addition to these forms, healthcare facilities may also need to submit other reports or documents to the PCB, such as:
- An annual report on e-waste and battery waste generation
- A list of designated collection points for e-waste and battery waste
- Proof of registration with a recycler or disposal facility
- Details of any incidents or accidents involving e-waste or battery waste
Healthcare facilities should consult with the PCB in their jurisdiction to determine the specific forms and reports that are required.
- Schedule I: Report on the generation, collection, and disposal of battery waste
Conclusion
The effective management of electronic and battery waste within healthcare facilities is paramount to mitigate environmental degradation and health hazards. Strategies outlined for e-waste encompass dedicated collection programs, waste reduction measures, segregation, audits, recycling collaborations, and community engagement.
Similarly, battery waste management strategies advocate for proper collection, education on handling and recycling, promotion of reusable batteries, and safety protocols. Compliance with governmental regulations, specifically adhering to policy guidelines and submitting requisite forms to the Pollution Control Board, ensures lawful and responsible disposal. Healthcare institutions must prioritize these practices, comprehensively managing e-waste and battery waste to minimize their environmental footprint and protect human health, thereby ensuring the ethical and sustainable disposal of these hazardous wastes.
References
- United Nations University (2023). The Global E-waste Monitor 2022. Bonn, Germany: United Nations University.
- United States Environmental Protection Agency (2023). A Guide to Electronic Waste Management. Washington, D.C.: United States Environmental Protection Agency.
- World Health Organization (2023). Electronic Waste and Health: Guidance for Healthcare Workers. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization.
- E-waste Management Rules, 2015, were published by the Government of India in the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change.