Strengthening Obstetric Care in Challenging Settings: Utilizing the WHO Checklist to Enhance Quality and Safety
Read the Magazine in PDF
Abstract :
Abstract:
This article summarizes the improvement journey of P.D. Hinduja Hospital & Medical Research Centre in enhancing the patient experience in the cashless insurance (T.P.A.) process. Through a comprehensive improvement plan, including process automation, streamlined communication, and better coordination, the hospital successfully addressed the root causes of patient dissatisfaction. Implementing these measures increased patient satisfaction, reduced visits to the T.P.A. desk, and improved trust in the staff.
Organization Profile
Sree Renga Hospital (SRH) is a multispeciality hospital located in Chengalpattu, a semi-urban area approximately 60 km from Chennai. With 47 beds, it serves nearly 75 villages in the vicinity. In 2012, SRH became the first NABH-accredited hospital in Tamil Nadu with fewer than 50 beds, meeting the primary standards. The hospital’s mission is to provide high-quality and affordable healthcare with honesty and accountability. SRH has introduced several pioneering initiatives in the district, including dialysis, diabetes, and an ISO-certified centre. It has also obtained accreditations from NABH, NABL, WASH, and Manyata. Supported by a renowned team of clinicians, surgeons, nurses, and paramedical staff, SRH is dedicated to patient-centric care.
Introduction
Providing safe obstetric care in resource-limited settings in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs) poses a significant challenge. The World Health Organization (WHO) developed the Safe Childbirth Checklist (SCC) to address this issue. This four-page checklist consists of 28 evidence-based essential birth practices that address the leading causes of maternal morbidity and mortality, intrapartum-related stillbirths, and neonatal deaths in healthcare facilities worldwide. This project aimed to adopt and customize the WHO Safe Childbirth Checklist to enhance the quality of obstetric care delivered at the hospital.
The disparity between current and desired performance in labour room practices necessitated a quality improvement (QI) initiative. Initially, the compliance rate with the Safe Childbirth Checklist (SCC) was 48%. To enhance adherence to standard practices, we embarked on implementing the SCC project.
The lack of a well-defined and structured multi-touchpoint workflow that accommodates obstetric care processes’ diverse needs necessitated implementing a modular solution. This approach aimed to enhance adherence to best practices at each touchpoint gradually. It was crucial to involve leadership in the project’s implementation and to maintain team motivation throughout the process.
Ensuring the timely completion of Partographs and preparedness to manage critical conditions such as Eclampsia, preterm premature rupture of membranes, postpartum haemorrhage, newborn resuscitation, and Kangaroo Mother Care were critical metrics in the Obstetric Care continuum that necessitated effective implementation.
To address these challenges, adopting a tested and standardized template encompassing various elements, including facility infrastructure, supply chains, teamwork culture, and quality improvement initiatives tailored to local contexts is essential.
The WHO Safe Childbirth Checklist (SCC) offers a flexible framework to enhance the quality of obstetric care across various healthcare settings. It was integrated into the Labour Ward Quality Improvement initiative, incorporating over 40 new clinical and operational items into the checklist to align with local regulatory and statutory requirements.

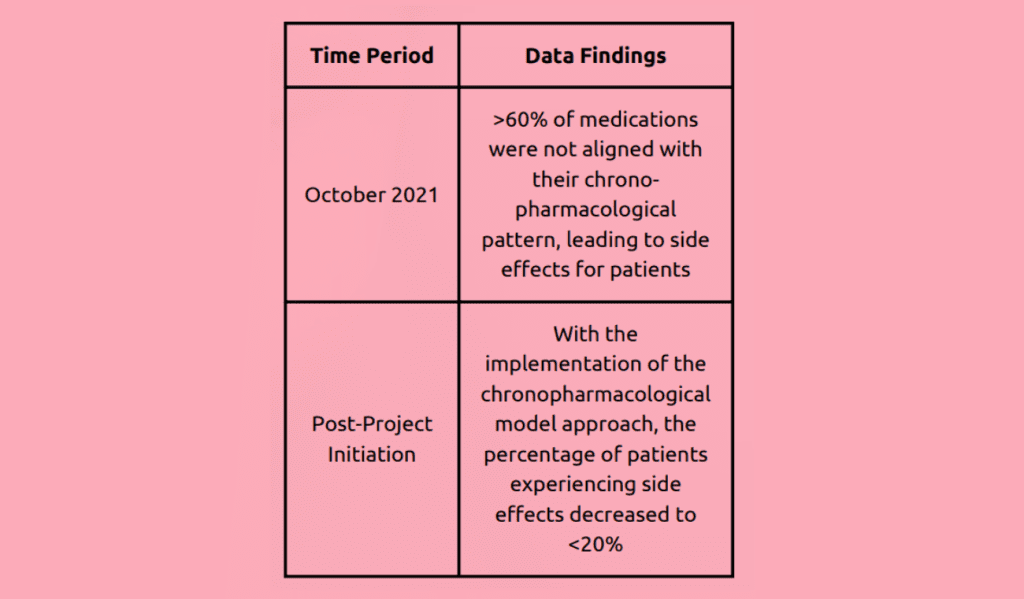
Before the introduction of chronopharmacology, the management of allergic rhinitis involved prescribing antihistamines twice a day, along with oral corticosteroids. Unfortunately, the adherence rate to this treatment regimen was less than 45%.
However, with the implementation of chronopharmacology, a new approach was adopted. Patients were prescribed antihistamines to be taken at bedtime, along with a morning dose of oral corticosteroids. As a result, the adherence rate significantly improved, reaching 85%.
Outcomes :
Conclusion :
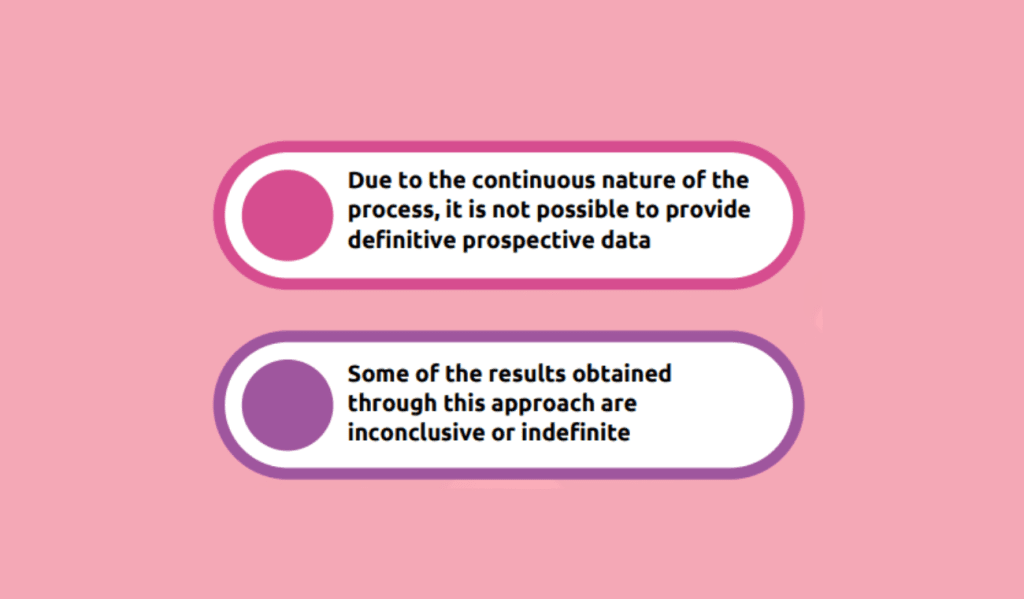
The implementation of chronopharmacology has shown promising results in optimizing treatment outcomes and reducing medication-related harm. The in-house Clinical Pharmacology Team is vital in identifying medications requiring timing adjustments based on chronopharmacological principles. Simultaneously, data capture and analysis provide valuable insights for further evaluation. The integration of chronopharmacology in inpatient and outpatient settings ensures targeted population outcomes. However, challenges exist in obtaining definitive prospective data, and the results obtained through this approach may sometimes be inconclusive. Nevertheless, chronopharmacology as a therapeutic approach holds great potential for improving medication adherence and patient well-being.