Colour Coding for Segregation of BMW
Read the Magazine in PDF
Abstract
Biomedical Waste Management is a critical process in healthcare facilities aimed at ensuring safe and responsible disposal of waste. This article discusses a comprehensive insight into the crucial steps involved in this process, emphasizing the significance of color coding for the segregation of biomedical waste.
The essential stages of biomedical waste management, starting from segregation at the point of generation, collection, and storage to pre-treatment, transportation, and eventual disposal. It highlights the necessity of compliance with basic tenets of biomedical waste management to guarantee safe handling and containment.
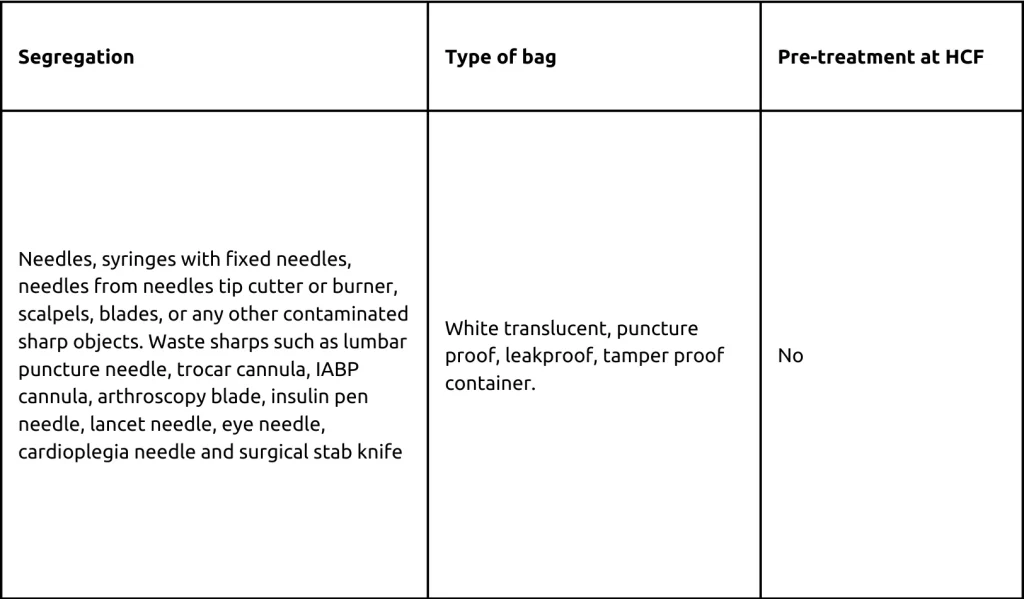
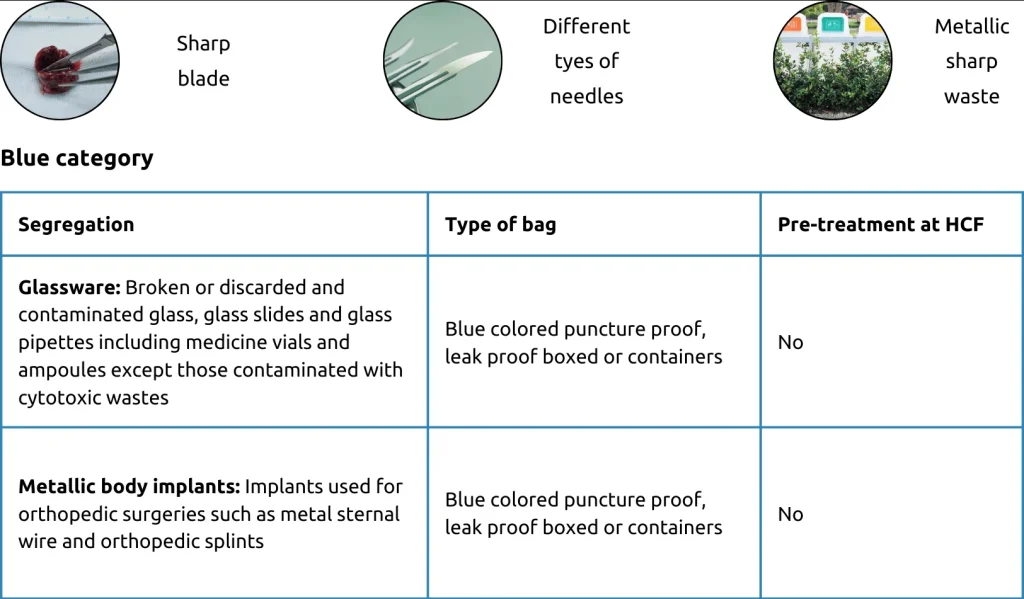
Furthermore, the document provides an in-depth breakdown of the various categories of biomedical waste as per the Biomedical Waste Management Rule, 2016, encompassing the yellow, red, white, and blue categories. Article underscores the importance of following proper segregation, packaging, and pre-treatment protocols for each waste type to ensure effective management.
Key considerations and guidelines, such as the treatment standards, dedicated equipment for
waste disposal, and suitable disinfection methods, are also elucidated in this comprehensive article.
The expertise and detailed insights serve as a valuable guide for healthcare professionals and facilities navigating the complexities of biomedical waste management.
Introduction
Biomedical waste management is a critical facet of healthcare operations, focusing on the safe and efficient disposal of waste generated in medical facilities. It encompasses a series of meticulous steps, from segregation and collection to treatment and disposal, aimed at minimizing health and environmental hazards associated with biomedical waste. Proper management is essential to ensure compliance with regulations and prevent the spread of infections, safeguarding both public health and the environment.
Steps involved in BMW Management
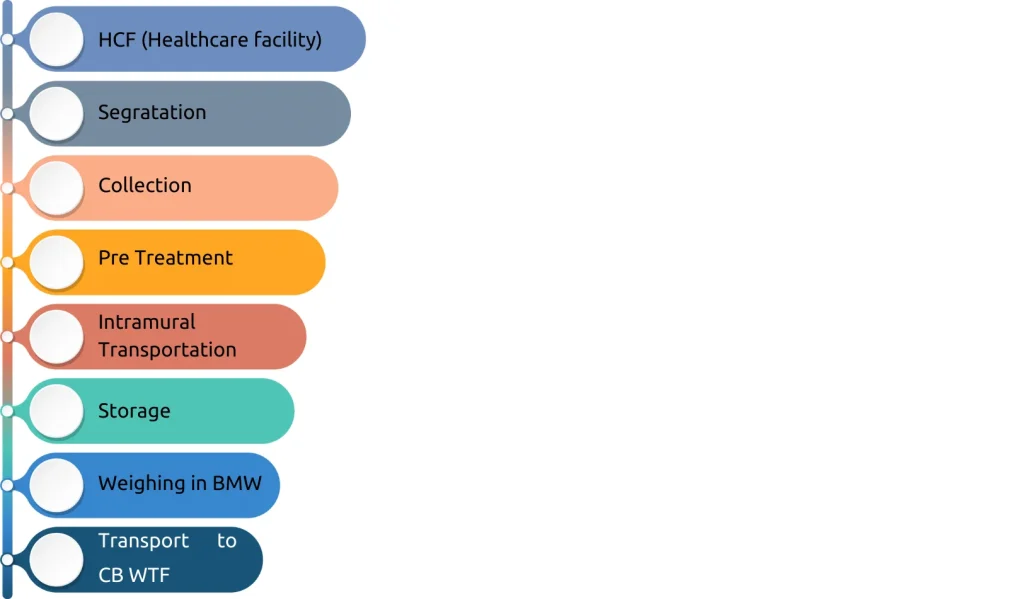
Biomedical waste management involves several crucial steps to ensure the safe and proper disposal of waste generated in healthcare facilities.
Here are the key steps:
Segregation: The first step is segregating biomedical waste at the point of generation. Waste
is categorized into different types (e.g., infectious, sharps, pathological, chemical, etc.) and collected separately using colour-coded containers or bags.
Collection and Storage: Segregated waste is collected in designated containers that comply
with safety standards. These containers prevent spillage, leakage, and exposure to waste handlers. The waste is stored temporarily in a secure area before further processing or disposal.
Pre-Treatment: The waste undergoes treatment to minimize its hazardous nature. Common treatment methods include incineration, autoclaving, microwaving, chemical disinfection,
and shredding. The goal is to neutralize pathogens and reduce the volume of waste.
Transportation: Collected waste is transported from healthcare facilities to treatment and disposal sites using specialized vehicles. These vehicles adhere to safety regulations to prevent spillage and contamination during transit.
Disposal: After treatment, the waste is safely disposed of following environmentally friendly methods. Disposal options include landfilling for non-hazardous waste, incineration for certain types of waste, and other approved methods based on regulatory guidelines.
Monitoring and Compliance: Continuous monitoring and compliance with regulatory standards are essential. Regular audits, inspections, and assessments ensure that healthcare facilities follow proper waste management protocols.
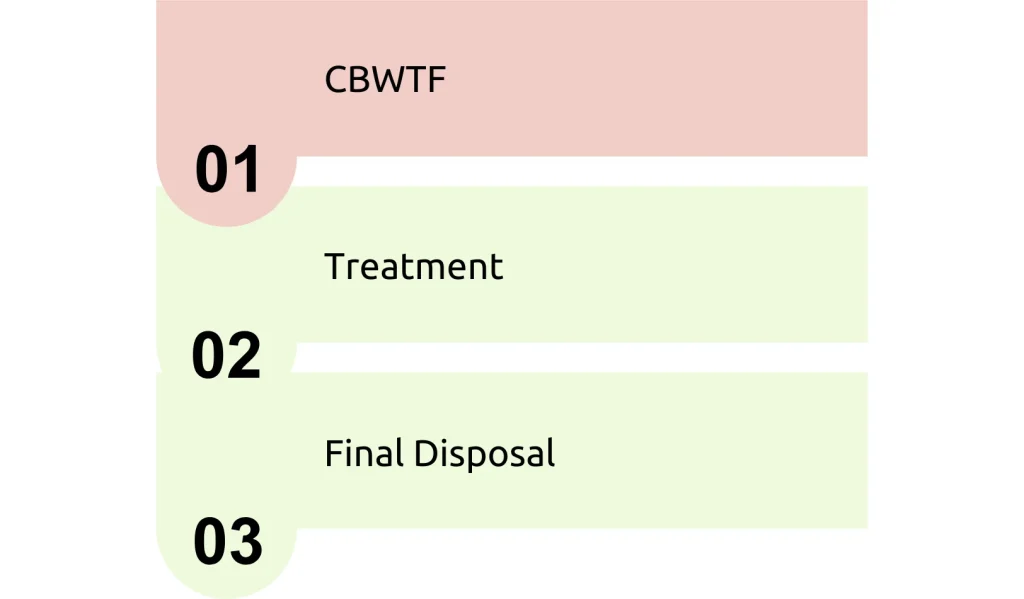
Basic tenets of BMW management
- Biomedical waste must be segregated at the point of generation of source
- Biomedical waste bags and sharps containers should be filled to no more than three quarters full.
- All the bags/containers/bins must be labelled with the symbol of biohazard or cytotoxic hazard.
- Interim storage-wastes from various departments must be stored in the dirty utility/sections.
- In house transportation of the waste from the site of generation/interim storage to central waste collection centre (CWC, situated within premises)
- Must be done in closed trolley
- Maintained in CWC until final treatment and disposal at CBWTF.
Categories of Biomedical Wastes
According to biomedical waste management rule, 2016, the biomedical wastes fall into four categories:
1. Yellow category
2. Red category
3. Blue category
4. White category
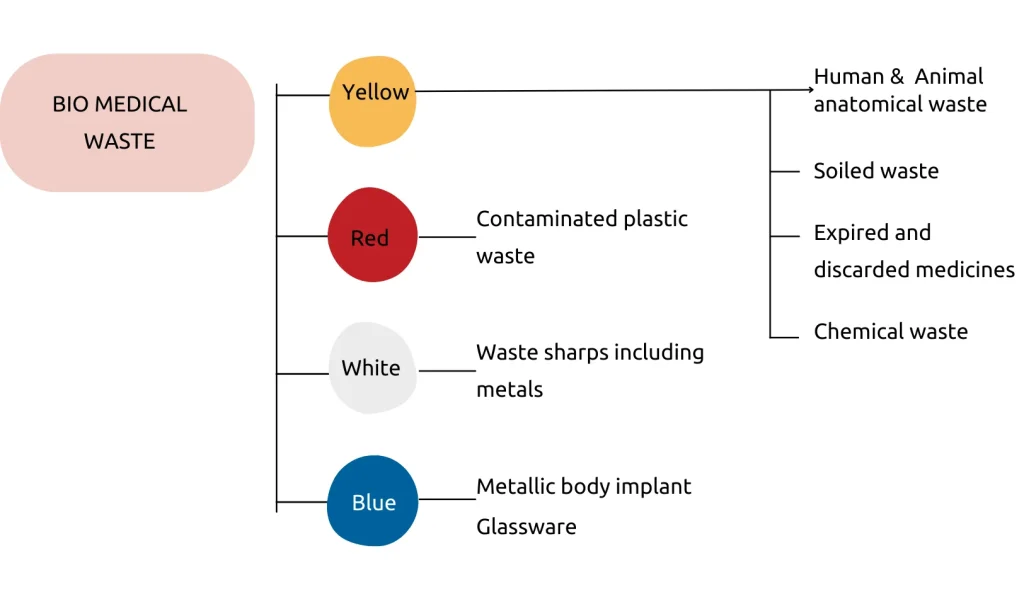
Yellow Category
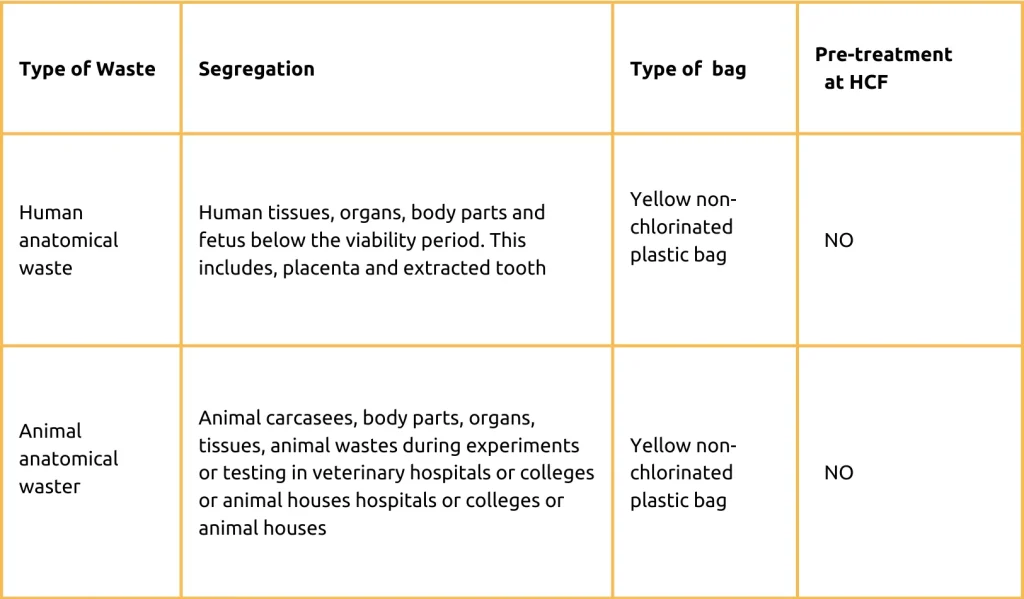
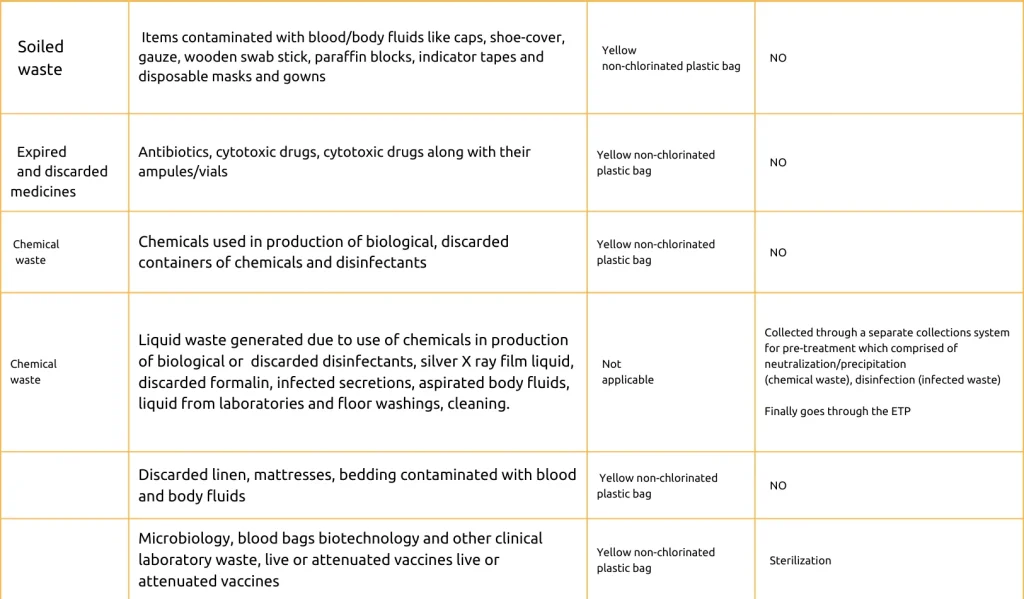
Red category
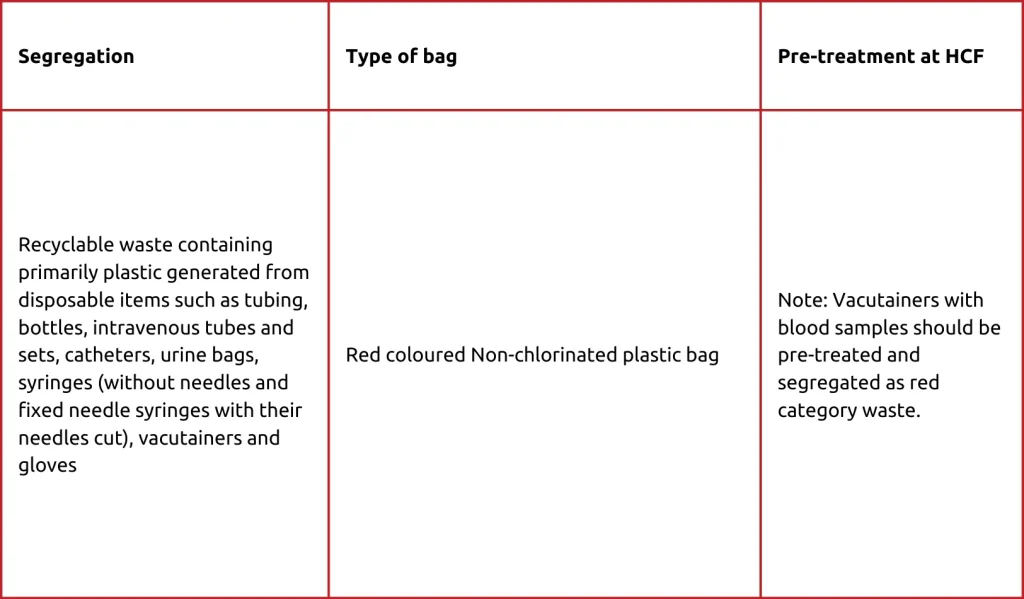
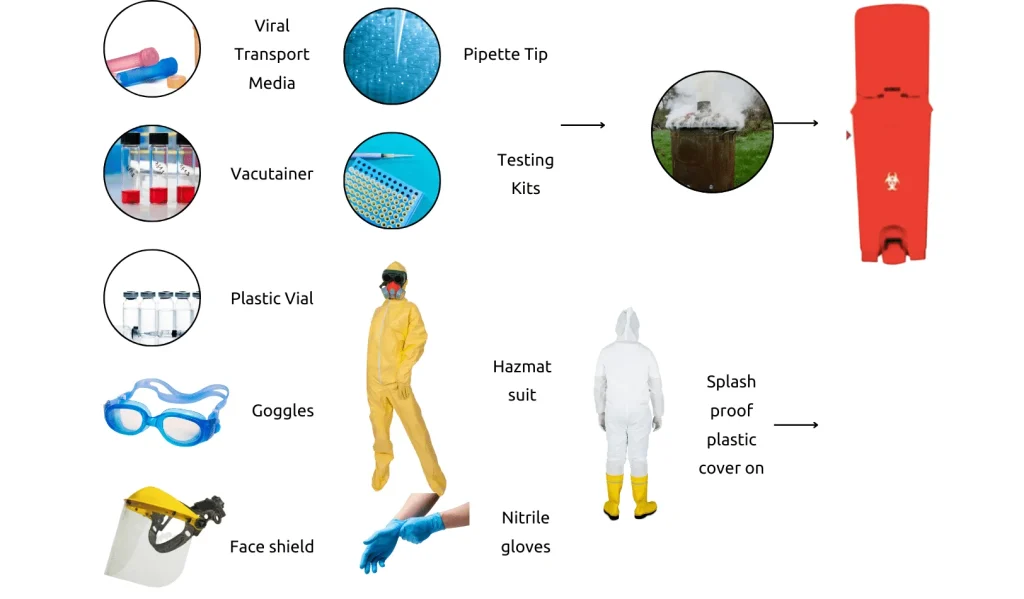
White Category

Important considerations
- The treatment of BMW must meet the standards as specified in BMW rule, 2016
- The autoclave used for sterilization of discard of blood bags, microbiology waste, including vials containing vaccine/positive controls must be dedicated for treatment of bio-medical waste only
- Chemical disinfections is to be performed by 1% hypochlorite solutions or equivalent disinfectant like aldehydes, lime, ammonium salts, phenolic compounds.
- Guidelines for management of healthcare wase as per biomedical waste management rule, 2016
- Pictorial guide on biomedical waste management rule 2016 (amended in 2018 and 2019)
Conclusion
In conclusion, Biomedical Waste Management provides a holistic understanding of the multifaceted process. The comprehensive overview, spanning from segregation to disposal and compliance, underscores the significance of adhering to proper protocols and guidelines. Emphasizing the importance of colour coding for waste segregation and compliance with the Biomedical Waste Management Rule, 2016, this article serves as an invaluable guide for healthcare professionals. The outlining of the critical steps involved in waste management ensures a safer and more efficient handling of biomedical waste in healthcare facilities, promoting a healthier environment and enhanced safety measures.
Author
-

HOD, Department of Pathology and microbiology and incharge infection control, breach candy hospital trust, Mumbai