Paving the way to Zero Harm : Enhancing Medication Safety
Read the Magazine in PDF
Abstract:
This article highlights the journey of Ruby Hall Clinic in Pune towards achieving medication safety and improving patient satisfaction. The organization recognized the impact of medication errors on patient outcomes and embarked on a comprehensive project to enhance medication management practices. By implementing various interventions, such as reasonable prescription practices, improved medication administration procedures, and training programs, Ruby Hall Clinic aimed to achieve zero harm from medication. The results showcased significant improvements in prescription, administration, storage, and dispensing compliance rates, along with a substantial reduction in medication transcription errors and medication errors. Additionally, the implementation of PRIME certification and the emphasis on patient safety contributed to enhanced patient satisfaction and better quality care. The project’s success demonstrates the organization’s commitment to continuous improvement in medication safety and patient care.
Organizational Profile:
In 1959, Ruby Hall Clinic established itself as a renowned provider of superior healthcare services in Pune, Maharashtra. With a substantial capacity of 800 beds, our hospital boasts a robust infrastructure that accommodates a wide range of specialities and super specialities. Our team comprises 300 consultants, over 650-panel doctors, and 2000 paramedical staff, ensuring comprehensive care across all departments.
In addition to the hospital, Ruby Hall Clinic has its own Nursing Institute, 17 Medical Centers and 24 diagnostic centres spread across Maharashtra. We prioritize quality improvement, personalized healthcare, and cutting-edge technology, making us Pune’s first nationally accredited multi-speciality centre. Among the few healthcare facilities in India, we proudly hold 7 NABH and NABL certifications, along with a cGreen OT certification for our operation theatres.
Equipped with an impressive range of resources, we provide compassionate, state-of- the-art care to a diverse patient population. Leveraging the latest advancements in science and technology, we cater to over 36,000 inpatients and over 1.4 lakh outpatients annually. Our services span various disciplines, including cardiac surgery, cancer treatment, organ transplants (kidney, liver, bone marrow, and heart), advanced neurosurgery, orthopaedics (hip and joint replacements), urology, bariatrics, IVF, high-tech imaging, and diagnostics. From head to toe, we cover a comprehensive array of medical specialties to meet the healthcare needs of our patients.
Introduction:
Medication errors resulting from unsafe medication practices harm patients, leading to adverse outcomes such as prolonged hospital stays, increased expenses, and even risks of morbidity and mortality. These errors often arise from deficiencies in medication systems, inefficient processes and policies, and human factors. The COVID-19 pandemic further highlighted the importance of prioritizing safe medication management and compelled us to focus more on medication safety.
Intending to achieve zero medication errors and ensure 100% patient safety, our management initiated an extensive project in January 2021. This project involves the active participation of key stakeholders in medication management, including pharmacists, doctors, nurses, HR personnel, clinical pharmacists, and the quality team. By bringing together these core stakeholders, we aim to strengthen our medication practices, enhance compliance, and establish robust systems and processes to mitigate the occurrence of medication errors.
Upon reviewing medication audit data and quality improvement trends, it was observed that compliance rates for various aspects of medication management were as follows: prescription compliance stood at 57%, administration at 65%, storage at 72%, and dispensing at 79%. However, there was a decline in staff knowledge regarding medication management policies, which dropped to 59%. Disturbingly, medication transcription errors significantly increased to 78%, and overall medication errors rose to 17% compared to the previous rate of 3%. These alarming figures indicate a compromised level of patient safety.
After conducting a root cause analysis and utilizing the 5 Whys technique, the following reasons and causes were identified as contributors to medication errors and reduced compliance with safe medication management practices:
- Multiple forms for medication management and non-uniform drug order writing locations affected compliance with excellent prescription writing. Medication transcription by junior doctors/nurses also contributed to errors.
- Inconsistent reconciliation of medicines at transit points impacted medication management.
- Challenges in medication administration included increased workload, lack of a designated medication preparation area, inadequate adherence to aseptic technique, compromised training during COVID leading to insufficient knowledge among newly joined staff, and separate documentation for drug administration.
- Decreased drug dispensing and storage compliance resulted from staff’s lack of knowledge on updated LASA/High-risk drug protocols, incomplete drug orders, illegible handwriting in prescriptions, and casual attitudes towards vague Narcotic medications.
- COVID-related disruptions affected staff training and education on medication management protocols, including policies on verbal drug orders, High Risk/LASA drugs, drug-food interactions, and reporting mechanisms for medication errors and adverse drug reactions.
- These factors collectively contributed to medication errors and compromised patient safety in medication management.
To address the identified problems, the following remedies were brainstormed and implemented:
- Prescription-related problems gaps
- Medication administration
- Conducted major drives
- Recruited a separate inpatient department (IPD) pharmacist
- Introduced allergy cards for patient information. • Conducted Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) for medication errors and adverse drug reactions (ADR).
- Provided digital drug references for doctors.
These measures collectively aimed to improve prescription practices, enhance medication administration procedures, raise awareness and education on medication safety, and implement policies and tools for effective medication management.
For maintaining the improvements made:
- Improvement actions were implemented using PDCA/DMAIC tools, including monthly audits of the prescription, administration, and dispensing processes, along with QI trend analysis and medication error reviews.
- Immediate actions were taken to address identified deviations, and the effectiveness of these actions was tested in subsequent audits and drives/campaigns.
- The project was implemented hospital-wide in all patient care areas and replicated in other branches of Ruby Hall Hospitals.
- A well-trained and skilled team was deployed to ensure successful project implementation and monitoring.
- Area-wise findings within the hospital were analyzed and reviewed separately to understand gaps and deviations better, enabling the development of targeted action plans for improvement.
Therefore, the project follows a systematic approach, continuously evaluating and refining medication management processes to achieve “Zero Harm from Medication.”
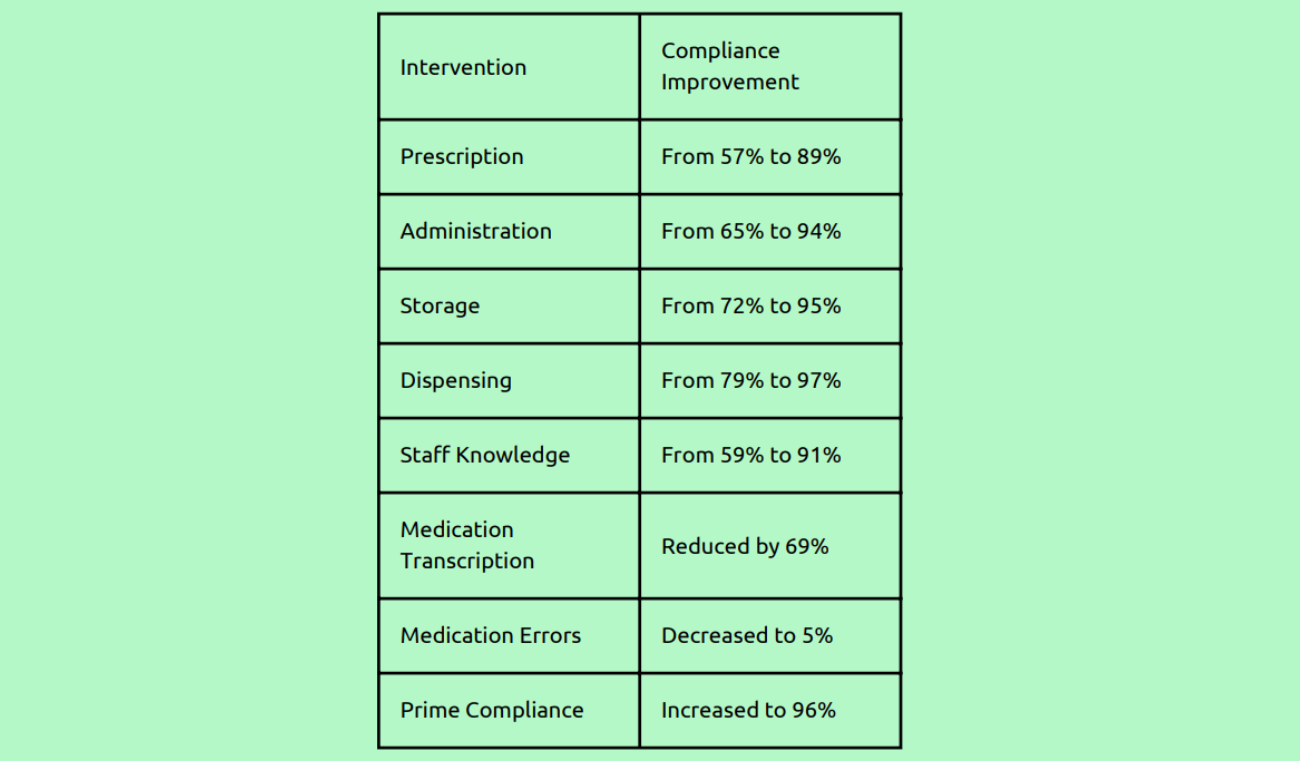
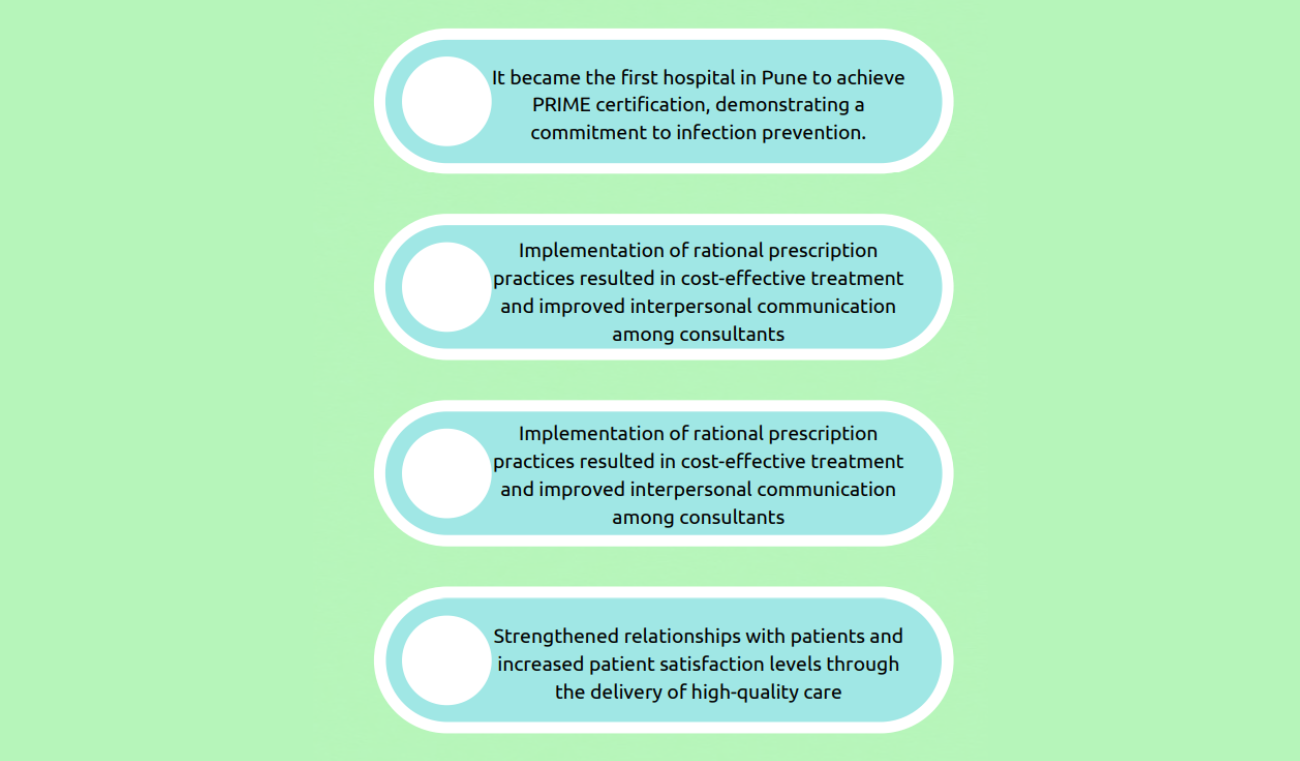
Conclusion:
The medication safety project undertaken by Ruby Hall Clinic in Pune has yielded promising results in improving patient safety and satisfaction. The organisation successfully enhanced compliance rates and reduced medication-related risks by addressing the root causes of medication errors and implementing targeted interventions. The implementation of PRIME certification and the emphasis on rational prescription practices further augmented patient safety. Through rigorous training, process improvements, and a culture of continuous improvement, Ruby Hall Clinic has made significant strides towards achieving zero harm from medication. The organization remains dedicated to maintaining and further improving medication safety, ensuring its patients’ highest quality of care.