Nutrition stewardship: A stewardship approach leading to reduce calorie deficit & ICU mortality rate
Read the Magazine in PDF
Abstract :
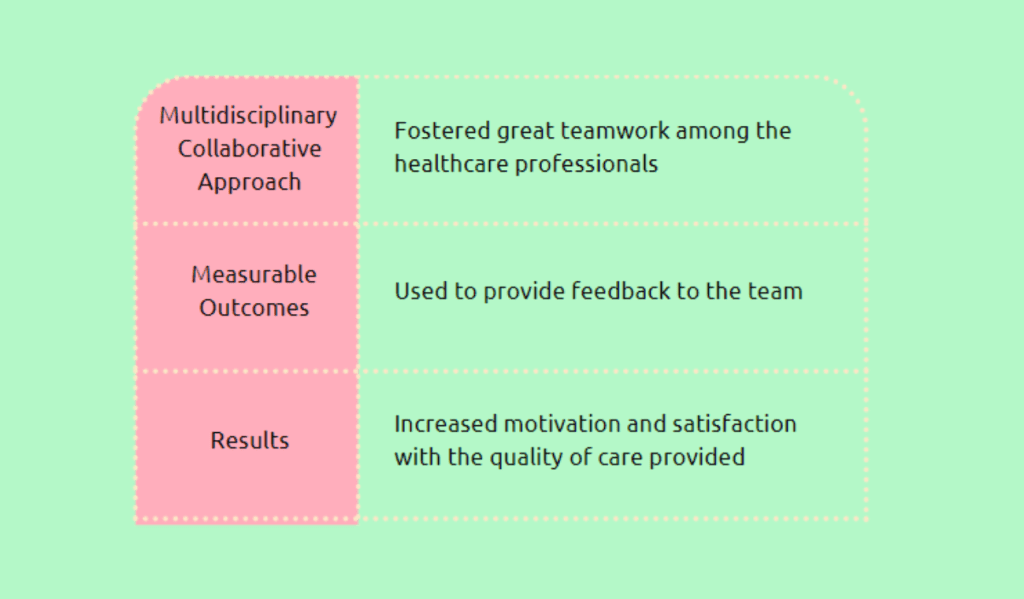
The article addresses the problem of malnutrition among hospitalized patients, particularly those confined to intensive care units (ICUs), and the Nutrition Stewardship Program put in place by the Sir H. N. Reliance Foundation Hospital in Mumbai to address this issue. The program intends to reduce energy and protein shortages, lower death rates, and shorten typical ICU stays. The program includes feeding barrier strategies, nutritional evaluation, prescription, and monitoring. Over seven months, the program reduced energy deficits by 49%, protein deficits by 76%, mortality rates by 19.14%, the average duration of stay in the ICU by 13.6 days, and fatality rates by 41.67%. Additionally, the program boosted cooperation, motivation, and satisfaction with the quality of care delivered.
Organization Profile
The Sir H. N. Reliance Foundation Hospital is a quaternary care hospital in South Mumbai with 345 beds. Its mission is to provide safe, affordable, and world-class healthcare to all members of society by utilizing international evidence-based practices through highly skilled professionals, well-trained staff, and the latest technology. The hospital has obtained JCI (Joint International Commission) and NABH accreditation, representing the highest quality care and patient safety standards. Additionally, it is the largest gold-certified green hospital in Mumbai, recognized for national and international green building conformance.
Introduction
Malnutrition is when the body does not receive the necessary nutrients to function correctly. It can result from various factors, including inadequate dietary intake, malabsorption, and increased nutrient requirements due to illness or injury. Malnutrition is a common problem among hospitalized patients and is particularly prevalent in those admitted to intensive care units.
The prevalence of malnutrition in intensive care units is as high as 40%. Malnutrition in critically ill patients can lead to a negative energy balance, resulting from the body using more energy than it takes in. A negative energy balance can cause muscle wasting, impaired immune function, and delayed wound healing.
Early nutrition intervention can help reduce the rate of complications, length of stay in the hospital, mortality rate, and cost of care. Providing adequate nutrition to hospitalized patients is essential to their nutritional status. Studies have demonstrated a significant inverse linear relationship between mortality and total daily energy intake. Thus, we hypothesize that all patients will have their dietary objectives established at the time of admission to the ICU. However, several problems, including fluid restriction, feeding intolerance, procedural fasting, and staff knowledge, may make it challenging to accomplish these objectives. Implementing a nutritional stewardship program in the ICU will improve the ability to establish and achieve the dietary goals set for the patients.
Therefore, in this study, we investigated the decrease in energy and protein deficits on discharge through nutritional stewardship and analyzed the impact on mortality and length of ICU stay.
Methodology
Implemented remedies: A nutrition stewardship program was implemented to address the issue of substantial energy and protein shortages in critically ill patients. Within the first 24 hours of admission, a dietician evaluated ICU patients’ nutritional health and demographic characteristics as part of the program. A cumulative protein and calorie deficit was determined on day three after admission.
A dietary prescription was created with the intensivist to optimize calorie and protein deficiencies, and daily checks were made to reduce these shortfalls. For procedural fasting, the program used catch-up match-up meals, hypercaloric formulas for fluid restriction, and parenteral nutrition for gastrointestinal intolerances as therapies to get over feeding obstacles. The program ensured that at least 70-80% of the daily nutritional requirement was met by the tenth day after ICU admission.
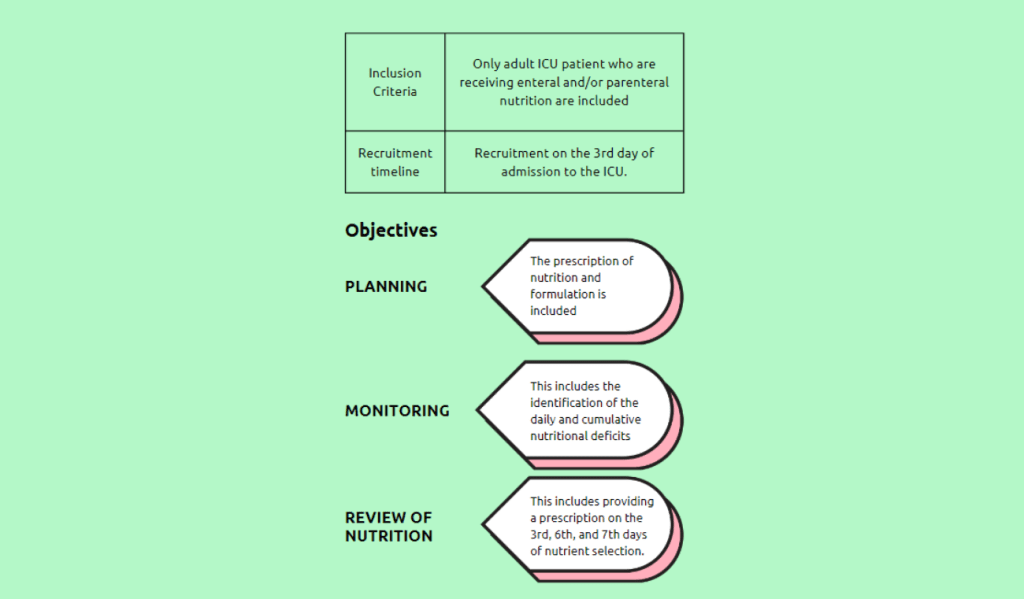
Maintenance of improvement:
Various measures have been implemented to maintain the progress achieved through the Nutrition Stewardship Program. To ensure ongoing monitoring and identify potential issues, the cumulative caloric and protein deficit is assessed on Days 6, 9, and 12 following admissions to the ICU.
This enables prompt intervention and the implementation of changes as needed. After being discharged from the ICU, each patient’s program results are also examined to ensure their dietary requirements are satisfied as they continue to recuperate.
Outcome
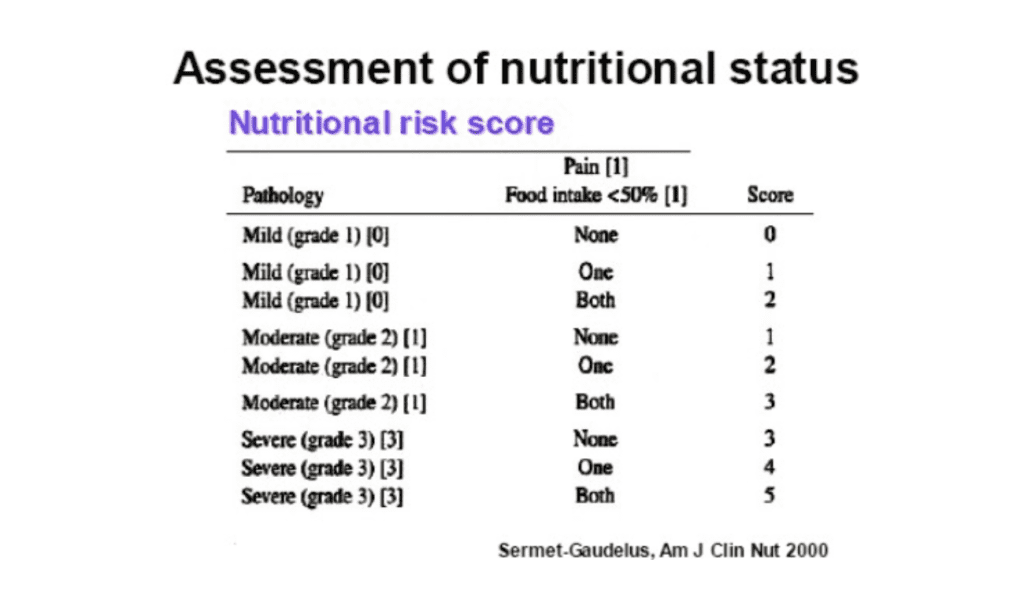
A total of 15 patients in the intensive care unit (ICU) were chosen for the study, and their selection took place on the seventh day of their hospitalization. Patients were enrolled on the third day of admission to the ICU to address the deficiencies. The baseline data collected were as follows:
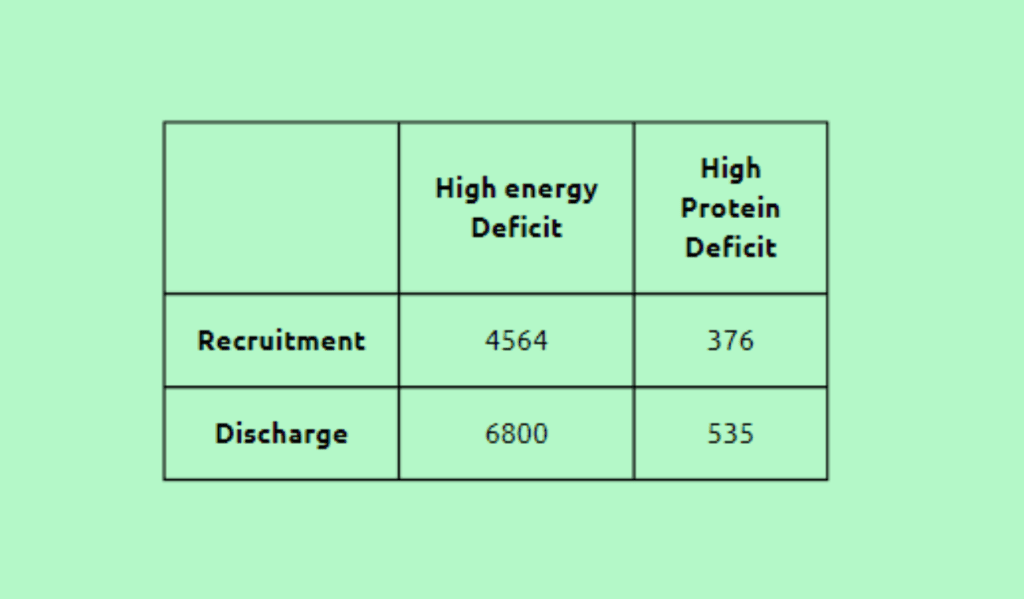
Based on the baseline data, the following targets were set:
- Analyze the nutritional assessment score.
- Implement nutrition stewardship by February 2022.
- Overcome feeding barriers and achieve a minimum 50% reduction in energy and protein deficits.
Following were the results after a period of seven months:
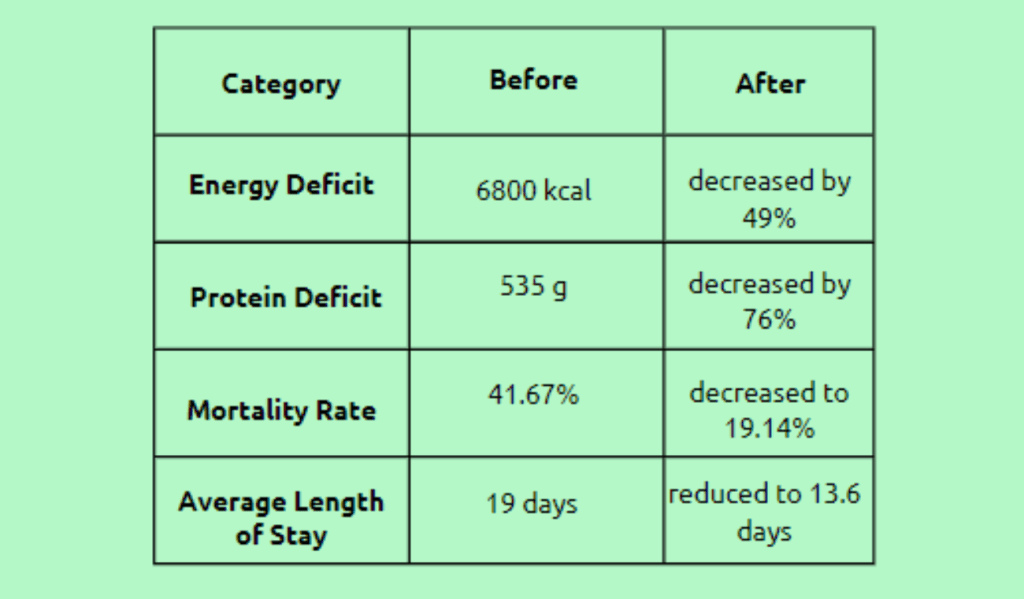
However, the below-mentioned results may be subjective, qualitative, or difficult to express in concrete terms. They often involve emotional well-being, satisfaction, perceptions, attitudes, or the overall impact on individuals or communities.
Cloning the improvement
By gathering crucial nutrition data, the RFH Nutrition app aims to replicate the success of the Nutrition Stewardship Program.
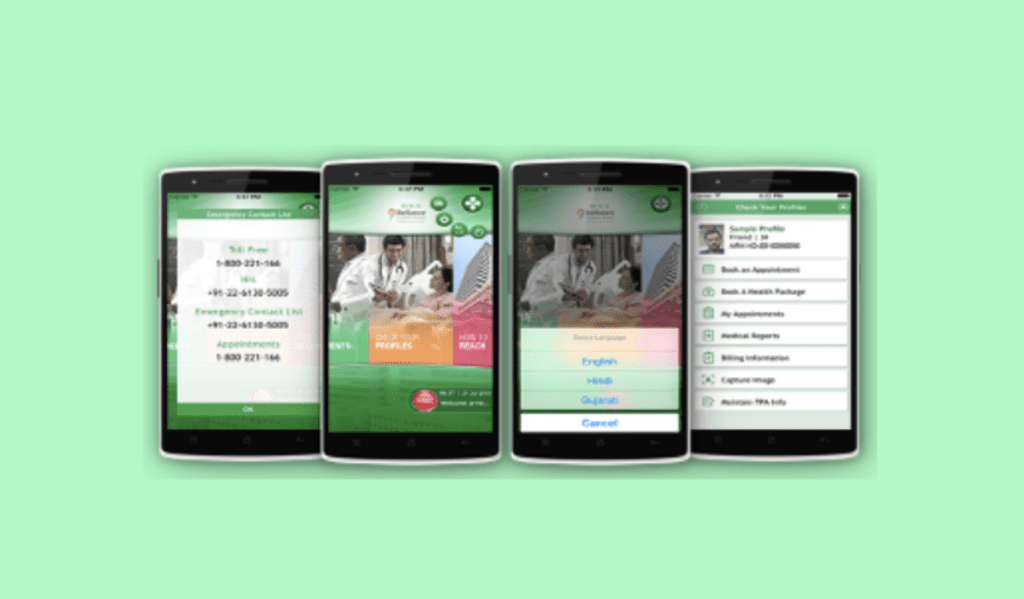
The application records the NRS Score, Nutrition Prescription, Nutrition Monitoring, Reassessment, and Nutrition Intervention. It will also make it possible to use the Pep-Up procedure.
Conclusion
The Sir H. N. Reliance Foundation Hospital is a renowned quaternary care facility in Mumbai committed to giving all societal members access to high-quality, secure, and reasonably priced healthcare. Hospitalized patients frequently experience malnutrition, which is more common in those admitted to intensive care units. The hospital created a nutrition stewardship program to address this problem, significantly reducing calorie and protein shortages and enhancing patient outcomes. A multidisciplinary collaborative strategy was used to carry out the program, which improved cooperation, boosted motivation, and raised satisfaction with the standard of treatment delivered. The hospital’s dedication to providing top-notch patient care is demonstrated by its JCI and NABH accreditations and its status as Mumbai’s largest gold-certified green hospital.