Chlorine Dioxide Water Disinfection System in Healthcare Facility: Experience Of A Tertiary Care Center
Read the Magazine in PDF
Abstract
AIG Hospitals, a prominent healthcare facility with a daily footfall of over 2,500 patients and extensive water infrastructure, faced a serious challenge in 2021 with Elizabethkingia Meningoseptica infections in its Intensive Care Units. Despite initial disinfection efforts, the persistence of biofilms in water distribution pipes allowed the bacteria to thrive.
This article presents the hospital’s journey in eradicating the infection, highlighting challenges faced, alternative solutions considered, and the ultimate implementation of a Chlorine Dioxide Dosing System. The IoT-enabled system significantly reduced the incidence of waterborne infections, emphasizing the importance of advanced water disinfection methods in healthcare facilities. This case study showcases AIG Hospitals’ commitment to patient safety and sets a precedent for the healthcare industry.
Introduction
AIG Hospitals, a leading healthcare facility with a substantial daily footfall of over 2,500 patients in outpatient services and more than 500 occupied beds faced a significant health crisis in early 2021.
The hospital’s daily water consumption stood at a substantial 400,000 litres, with an 800,000-liter storage capacity and a sprawling network of water pipelines stretching over 7 kilometres across the facility’s 1.2 million square feet of area. These pipelines had over 2000 delivery ports, making it a complex infrastructure to manage. These pipelines had over 2000 delivery ports, making it a complex infrastructure to manage.
During February 2021, AIG Hospitals reported several cases of Elizabethkingia Meningoseptica infection in their Intensive Care Units (ICUs). A total of 10 cases were documented between March and May 2021, which raised concerns about the safety of the hospital’s water supply.
Surveillance swab cultures revealed the presence of Elizabethkingia in the tap water of some ICUs. This bacterium, a common environmental microbe, is often found in hospital water supplies, making it a significant concern.
Problem Statement
The problem statement was clear: to eradicate the incidence of Elizabethkingia Meningoseptica infection, a waterborne bacterium, from the hospital. The initial actions taken by the Facility Management Team included upgrading water disinfection methods, but these proved ineffective.
A more profound investigation revealed that biofilms were still present in the hospital’s water distribution CPVC pipes, providing a haven for the bacteria. Until these biofilms were removed, the infection risk persisted.
Challenges Faced
Addressing this issue was far from simple, as the facility had high patient footfall and occupancy rates. Interrupting the water supply, even for a few minutes, was not feasible.
Moreover, the extensive 7-kilometre pipeline network had only one water supply valve per floor, lacking branch valves for phase-wise isolation.
Exploring Alternatives
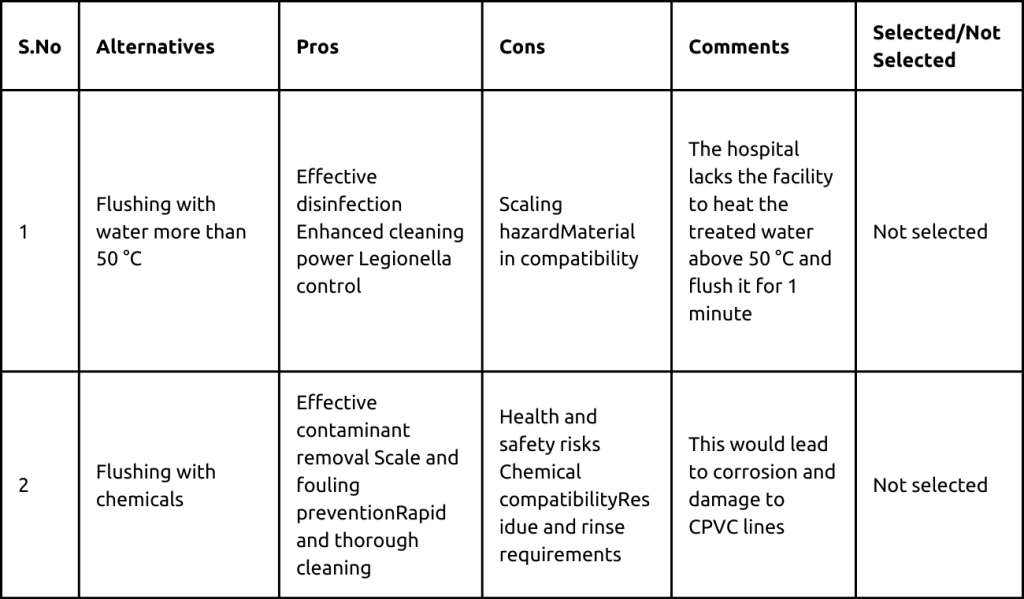
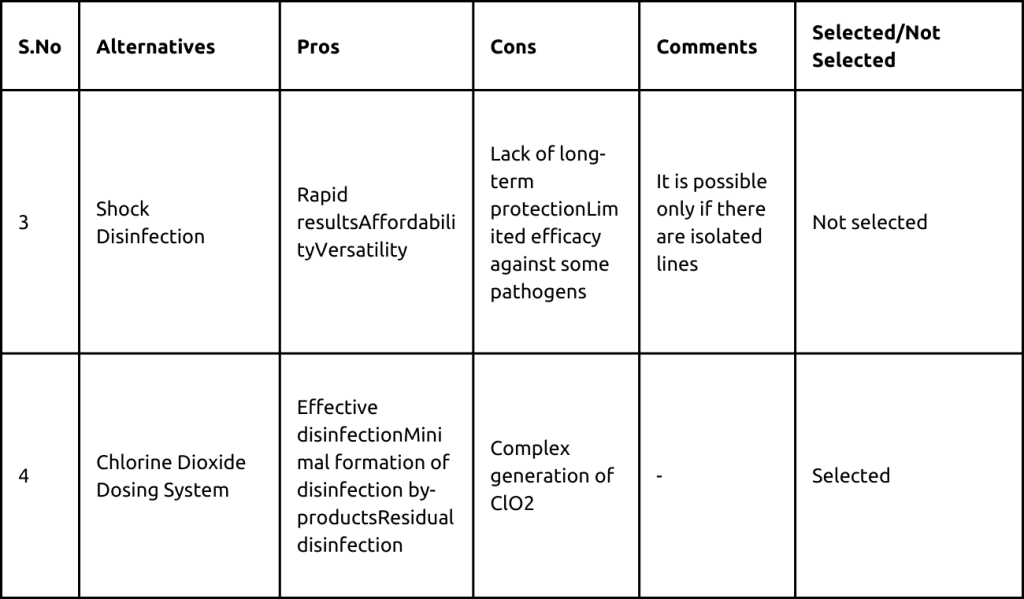
The team considered various alternatives to address the problem.
The Technology: Boom-OX Stabilized Chlorine Dioxide
AIG Hospitals chose the Boom-OX Stabilized Chlorine Dioxide System, an IoT-enabled system that mixes chemicals according to predefined values at the water distribution points.
This system enabled chlorine dioxide to circulate throughout the CPVC pipes, ensuring comprehensive disinfection. The Oxidation Reduction Potential (ORP) Meter managed the entire system, maintaining ideal sanitation and safe consumption conditions.
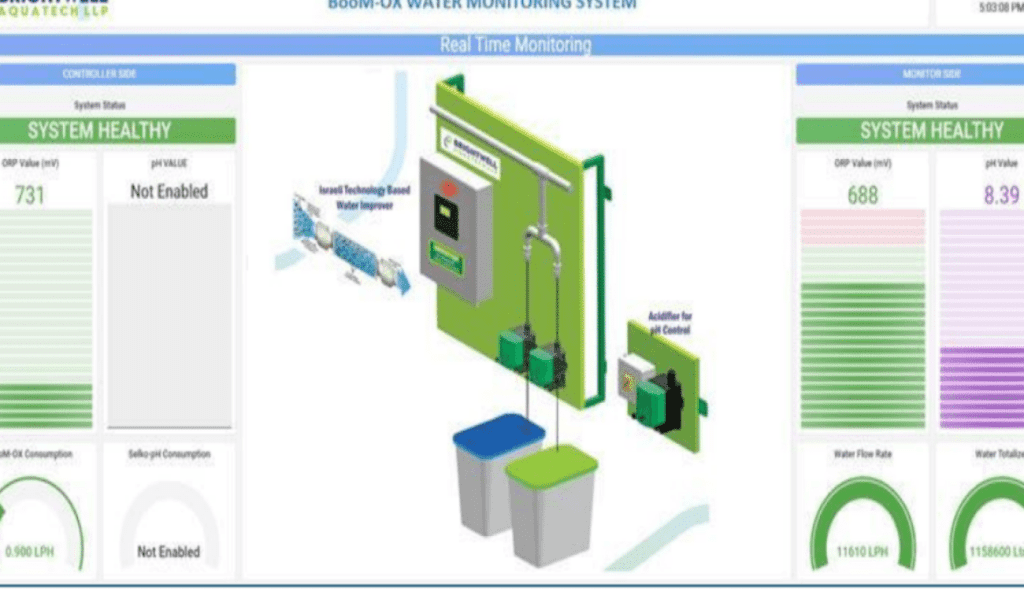
Implementation and Impact
The system was installed in January 2023, and within two days, it brought about a notable change. The water at the terminal ends of pipes initially turned dark-brownish, a result of biofilm residue. To eliminate this, daily flushing was done every two hours for 15 days. After this initial phase, the water at the terminal ends remained clear, free from discoloration, and, most importantly, infection-free.
Water analysis reports before and after the installation of the Chlorine Dioxide Dosing System revealed a significant reduction in waterborne organisms in clinical areas, particularly where biofilm formation was present. For example, the incidence of Elizabethkingia decreased from 16 cases in 2022 to only 3 in 2023.
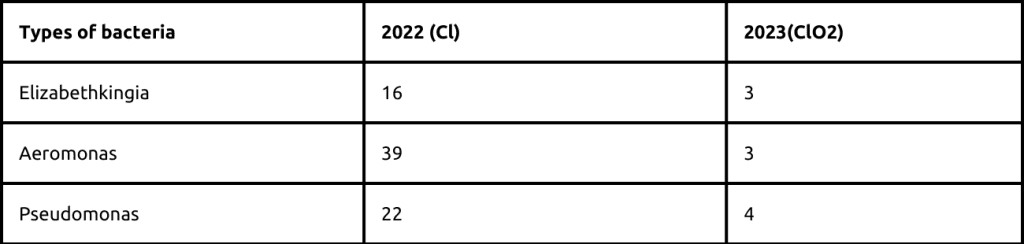
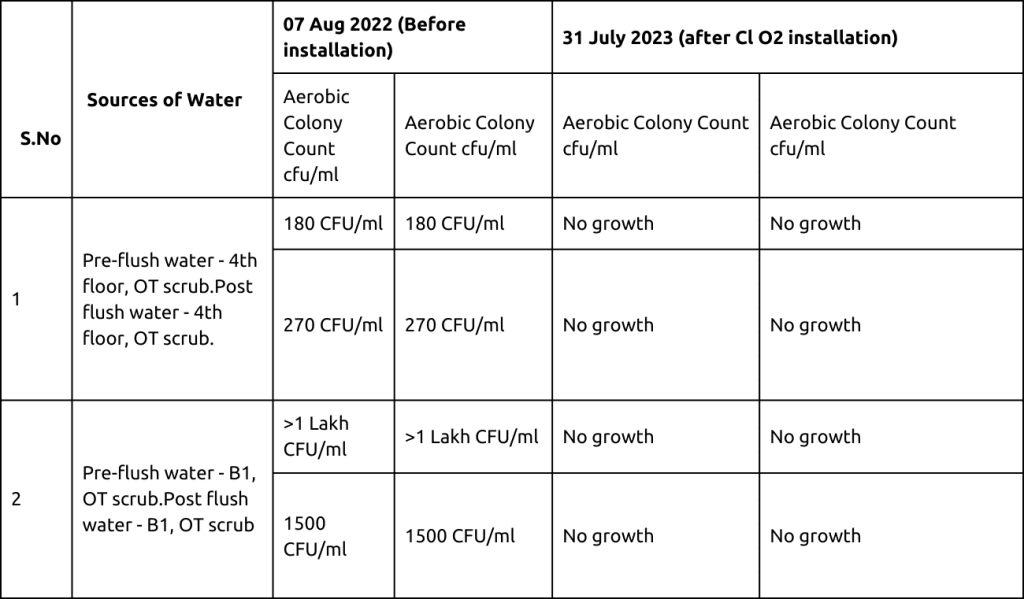
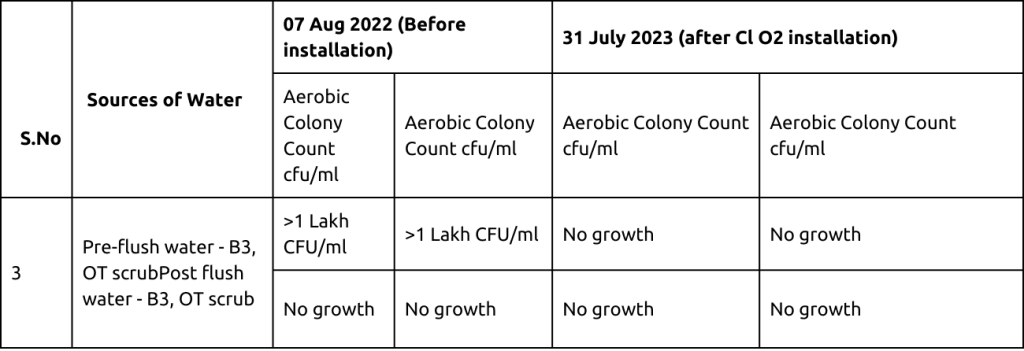
Conclusion
The successful implementation of the Chlorine Dioxide Dosing System at AIG Hospitals demonstrates the importance of advanced water disinfection techniques in healthcare facilities. The hospital’s proactive approach to resolving the Elizabethkingia Meningoseptica infection issue has not only protected patients but also set a precedent for water management in the healthcare industry. It serves as a remarkable case study in the battle against waterborne infections, highlighting the importance of staying up-to-date with modern technology and continuously striving for the safety and well-being of patients.