Sustainable Future – Kempegowda International Airport Bengaluru (KIAB)
Read the Magazine in PDF
Introduction
Kempegowda International Airport Bengaluru (KIAB), or BLR Airport, is among the world’s busiest and fastest-growing airports, with 33 million annual footfalls. With a vision to enable journeys, create experiences and touch lives as the new gateway to India, BLR Airport, operated by Bangalore International Airport Limited (BIAL), has witnessed tremendous growth and evolution in the last few years. It has also set a standard for itself and the industry regarding sustainable practices.
The sustainability vision, ‘Touch lives by nurturing a sustainable future through initiatives that drive economic, social, and environmental transformation,’ is an apt corollary to BIAL’s vision. Supporting this vision is the sustainability strategy that has impeded its growth. At the core of BIAL’s sustainability journey are six pillars that form the roadmap to a brighter future: Water Stewardship, Net Zero Carbon Emission, Community Aligned Noise Management, Circular Economy, Sustainable Procurement, and Sustainable Mobility. These pillars are supported by the airport’s core values of Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR), Behavioral Change, and Compliance. This strategic framework directly contributes to 11 of the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals (UNSDGs) and indirectly to the other six UNSDGs. BIAL is also a signatory to the United Nations Global Compact initiative — a voluntary leadership platform for developing, implementing, and disclosing responsible business practices.
Net Zero Journey
BLR Airport is committed to achieving Net Zero Emissions (Scope 1&2) by 2030. Ours is a science-based approach to reducing and sequestering residual carbon emissions through afforestation initiatives and green vehicle adoption.
We are consuming 100% renewable electricity for our operations. BLR airport is equipped with renewable electricity infrastructure onsite and has explored offsite options for its airport operations. A combination of onsite Solar Plants and offsite (Open Access) Solar, Hydel and Wind Power PPAs have eliminated carbon emissions of more than 70,000 metric tonnes per year to achieve the objective of 100% Renewable Electricity generation and zero scope 2 Carbon emissions.
BLR Airport also achieved ACI’s highest Level 4+ Transition and Green Airports Recognition under the Airport Carbon Accreditation (ACA) program. This prestigious accreditation, led by the Airports Council International (ACI), reflects BIA’s unwavering commitment to efficient carbon management and sustainability.
BLR airport is focusing on a significant reduction of scope 3 emissions. Through stakeholder engagement and collaboration,>90% utilisation of Bridge Mounted Equipment (BME) – Fixed Electric Ground Power (FEGP) is achieved, leading to emission reductions. Sustainable mobility is a key focus area across BLR airport. BLR airport had committed to equipping 10% Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF) BY 2030.
Water positive
While achieving Net Zero Emissions is one of the primary goals, BLR Airport is also committed to responsible water consumption and replenishment that is socially equitable, environmentally sustainable and economically beneficial. With this objective, the organisation has always focused on building Sustained Water Positivity, considering future terminal expansions. With its processes, BLR Airport has achieved a water positivity index of 2.36, which means the airport replenishes more water than it consumes. The communities around have benefitted from the water conservation initiatives, and the region has transformed from being water scarce to an area that has developed and flourished. We have also implemented rainwater harvesting infrastructure to recover potable water through treatment. Currently, one-third of our potable water requirement is met through a rainwater treatment system, and we will move towards nearly 100% in the foreseeable future.
In addition, cutting-edge conservation technology is implemented to save water across both terminals. All the terminal washrooms have fixtures that use less water. The green landscape is maintained by a weather-based Smart Automatic Irrigation System controlled by a smartphone app, making it the first of its kind. To water plants efficiently, it analyses factors such as evapotranspiration, moisture in the soil, and the weather. With this system, the airport can save more water than traditional methods.
Terminal 2
With the new Terminal 2 (T2), BLR Airport has presented a terminal that’s sustainable, modern, and technologically advanced while rooted in its culture. The four pillars that have inspired T2 are Terminal in a Garden, Sustainability, Technology, and Art & Culture. The essence of these pillars has been captured throughout the design, architecture, and processes at the new terminal. T2 was planned, designed and built to be a sustainable building. It has been awarded the LEED Platinum Pre-certification* from USGBC (U.S Green Building Council), the largest airport in the world, to be certified before the commencement of operations. Terminal 2 has also received the prestigious IGBC Platinum certification from the Indian Green Building Council under the IGBC Green New Building rating system. Using natural building materials, harvested rainwater, recycled and treated wastewater, and natural light filtering through the skylights contribute to the sustainable nature of T2.
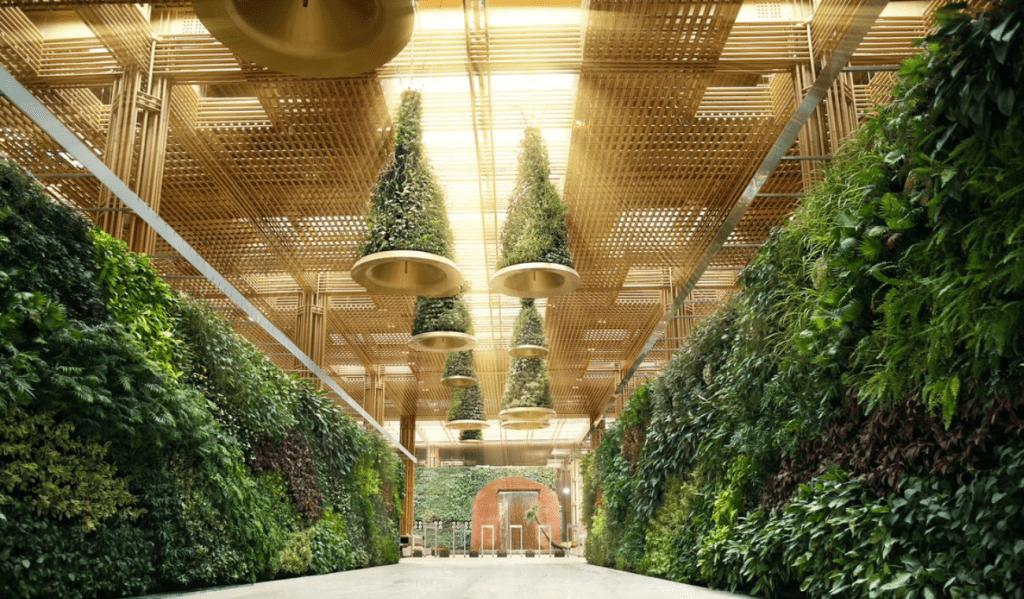


Here are a few highlights of the new terminal:
•10,000+ sqm of green walls/hanging gardens and outdoor gardens
•Many trees aged between 300 to 800 years have found a new home at the Terminal Forest
•Use of natural lighting during the day
•Skylight area of 10,494 sqm, around 12% of roof area
• Energy-efficient chillers, pumps and systems
•Recycling 100% treated wastewater
•Harvested rainwater for consumption
•Implemented Erosion & Sedimentation Control (ESC) measures
•Vegetation overbuilt structures account for 31% of the total site area
Environmental and ecological balance
While the aviation industry is working towards minimising its impact, BLR Airport has implemented processes to mitigate the adverse effects of its energy consumption. The environmental responsibilities were carefully managed throughout the entire process of setting up the airport.
To lower the amount of energy required for cooling, chiller plants with high efficiencies are utilised, and this plant optimisation has resulted in savings of over 1.7 million kWh. Through its energy conservation, BLR Airport has saved 2.2 million kWh of energy every year, enough power to supply 9,000 homes with electricity for one month. LEDs are used to illuminate the runways and streetlights around the area. The newly commissioned South Runway Airfield Ground Lighting is powered with LED lights, making it the first airfield in India to be fully powered with LED lighting. The recently refurbished North Runway is also powered with LED Airfield Ground Lighting. The entire apron’s high mast lights have been converted to LED lighting. This helps to conserve energy without compromising lighting quality or visibility. In 2020, BLR Airport achieved one of its goals of becoming Energy Neutral.
While energy consumption may be a primary concern, as a travel hub that operates 24/7, facilitating the movement of millions of passengers every year, another crucial aspect of environment management that needs particular attention – is the use of plastic; BLR Airport retailers are strongly encouraged to use bagasse packaging because it is 100 per cent biodegradable and compostable. Single-use plastics are no longer allowed in airport retail, food, and beverage establishments.
While passenger-facing measures are visible at the terminals, sections of the airport campus roads have been constructed using plastic waste – for the first time in the industry. Following the success of a trial road that utilised plastic waste replacing 6% bitumen, the airport constructed polymerised roads capable of withstanding adverse weather conditions. Electronic charging pods are installed at various points on the campus for EVs, facilitating sustainable mobility. Moreover, the campus has been much greener, with several trees planted from different species.
Landscaping and greenbelt development are among the most important aspects of reducing air, water and dust pollution; BIAL has focused on landscaping since the Airport’s inception 15 years ago. Bengaluru, known as the Garden City of India, has tried to reflect this image at the Airport by creating world-class gardens and green spaces around the campus. Our newly operational T2, a Terminal in a Garden, is a dedication to Bengaluru. Our full-fledged Landscape Department is vital in aesthetic improvement through landscaping, planting trees and shrubs along the roads, parking areas and office buildings. Along with improving the green aesthetics, they are instrumental in controlling soil erosion and creating a micro-climate around the airport campus with their in-depth understanding of the landscape. Greenery facilitates the survival of local flora and fauna and a healthy working environment for employees, stakeholders, customers and airport users.
Community development
BLR Airport’s steadfast commitment to sustainability is a fundamental principle ingrained in its business philosophy. Its sustainability-centric practices enforce policies and design interventions that architects, designers, engineers, concessionaries, and developers adhere to, aligning with the company’s holistic vision of sustainable development.
Besides making the airport a sustainable entity, BIAL is also working on making the region and communities around it self-reliant. The Kempegowda International Airport Foundation (KIAF), a Bangalore International Airport Limited (BIAL) subsidiary, was incorporated in March 2020 under Section 8 of The Companies Act 2013 as a Non-Profit Organisation. The Foundation’s main objective is to create social value through targeted interventions for communities around the Airport and the social ecosystem.

Author
-

Head Sustainability Bangalore International Airport Limited (Operator of Kempegowda International Airport Bengaluru)