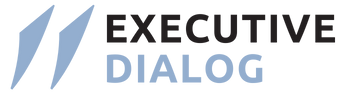Collaboration – Leveraging Technology
Read the Magazine in PDF
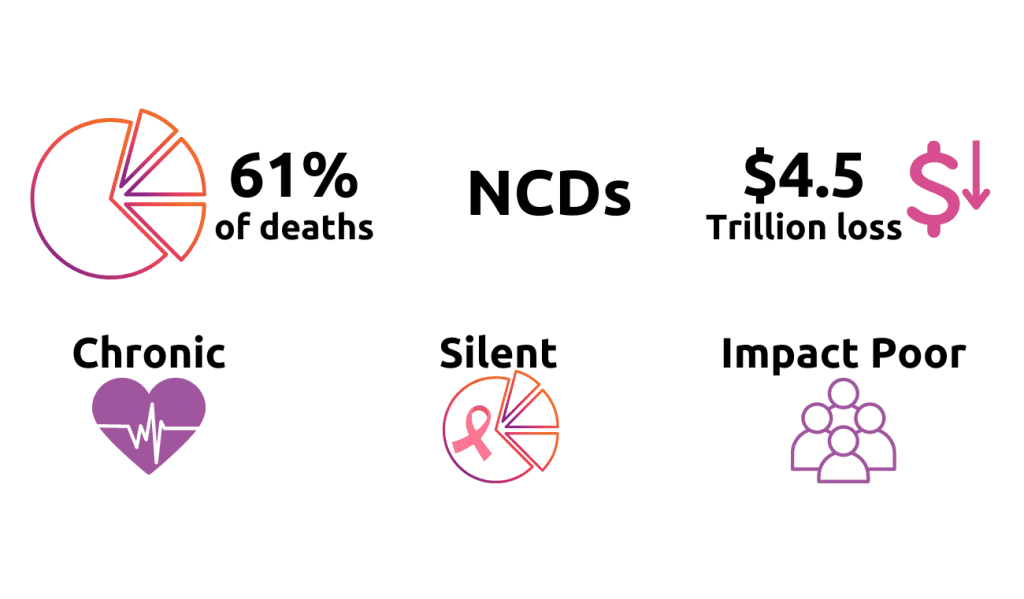
India's healthcare system encompasses various tiers of health workers, from ASHA volunteers to specialized centers and tertiary hospitals.
By - Ms Sunita Nadhamuni
Abstract
The article discusses the collaboration between the Indian government and a technology company to address public health challenges in India, focusing on the transition from communicable to non-communicable diseases as the largest health burden. The National Program for Prevention and Control of Cancer, Diabetes, Cardiovascular Disease, and Stroke, delivered through a tiered system, aims to reach more than 350 to 500 million individuals by leveraging technology and collaboration. it also highlights the importance of the continuum of care in healthcare, which ensures that patients comply with their treatment plan, and how technology plays a pivotal role in enhancing patient outcomes and improving the productivity and quality of care that healthcare providers deliver.
India’s public health sector is encountering a range of difficulties, notably the shift from infectious ailments to non-communicable ailments, which are currently the primary health concern. In response to this issue, the Indian government has implemented the National Program for Prevention and Control of Cancer, Diabetes, Cardiovascular Disease, and Stroke. In 2018, this initiative was revamped to become a population-focused screening and management program that aims to reach more than 350 to 500 million individuals.
In this particular situation, the government was interested in exploring how technology could be used to address public health issues, and a technology company became involved in the process. The company worked alongside the government to implement the program as part of its ESG initiative, which focuses on environmental, social, and governance matters. The company’s overall mission is to use technology to drive human progress, and the public health program is a prime example of how technology can be leveraged to tackle public health challenges on a large scale.
The program is designed with a tiered approach that begins at the village level and focuses on preventive screening for five specific diseases: hypertension, diabetes, total breast cancer, and cancers. Despite progress made, managing these diseases remains difficult due to their chronic nature. Patients require ongoing treatment that can last for months or even years. Unfortunately, only a small percentage of patients with these conditions are currently under control, leaving them vulnerable to the negative effects of their illnesses. Survival rates for these diseases are low, with rural areas being disproportionately impacted. Multiple factors are contributing to these challenges, including environmental conditions, social determinants (such as awareness, nutrition, and overall health-seeking behaviour), and low birth weight, which makes certain populations more vulnerable.
Recognizing the role that technology can play in addressing these challenges, the government and the technology company aimed to collaborate and leverage technology to drive progress. In India, the public health sector is facing several challenges, with the transition from communicable to non-communicable diseases representing the largest disease burden today. To address this, the government has launched the National Program for Prevention and Control of Cancer, Diabetes, Cardiovascular Disease, and Stroke. A technology company has partnered with the government to drive progress in implementing this program by leveraging technology and collaboration. The program is delivered through a tiered system, starting at the village level and focusing on preventive screening for five diseases.
Overall, the government and the technology company aim to use technology to address public health challenges and promote human progress.
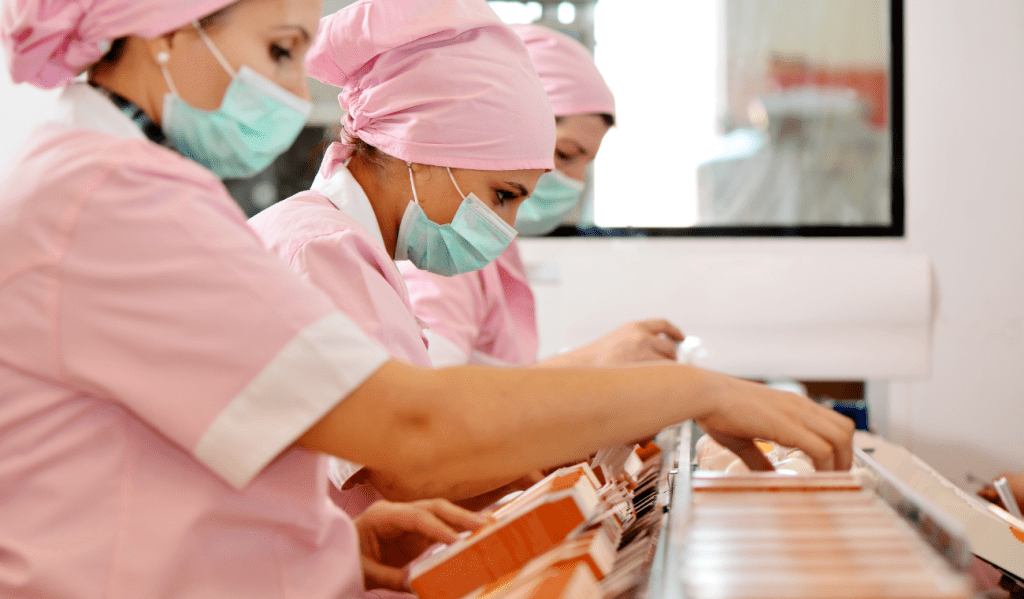

The healthcare systems are crucial elements of society as they guarantee that communities can access high-quality health services. In India, the health system consists of different levels of health workers, ranging from community volunteers known as ASHA workers to primary health care centres, specialized centres, district hospitals, and tertiary hospitals. With more than 150,000 health facilities nationwide, the health system offers an extensive range of services, such as non-communicable diseases and drug delivery. Nevertheless, the system confronts several obstacles, including deficient infrastructure, insufficient competence of health workers, and governance and standardization concerns.
Eight years ago, an initiative was launched to tackle these issues and create a digital suite of apps and a platform. The software system was created to offer a continuum of care for individuals and address the challenges faced by the health system. The primary aim was to enhance the delivery of health services and take a more proactive approach to healthcare by improving care standardization, increasing access to health services, and strengthening the visibility and accountability of health administrators. The Indian health system plays a critical role in ensuring that communities have access to quality health services.
Despite facing various challenges, India is making progress in improving the delivery of health services through initiatives such as the development of digital suites of apps and platforms. By striving to improve the health system continually, India is working towards a healthier and more prosperous future for its citizens.
Continuum of Care: The Importance of Adherence in Healthcare
The healthcare system is a complicated entity that necessitates a coordinated effort from multiple stakeholders to guarantee that patients receive optimal care. Regrettably, many patients fail to receive the care they require, and their treatment is not as efficient as it could be. This is where the concept of a continuum of care becomes essential. The term “continuum of care” pertains to a comprehensive and coordinated approach to providing continuous care to a patient from the moment of diagnosis to the completion of treatment.
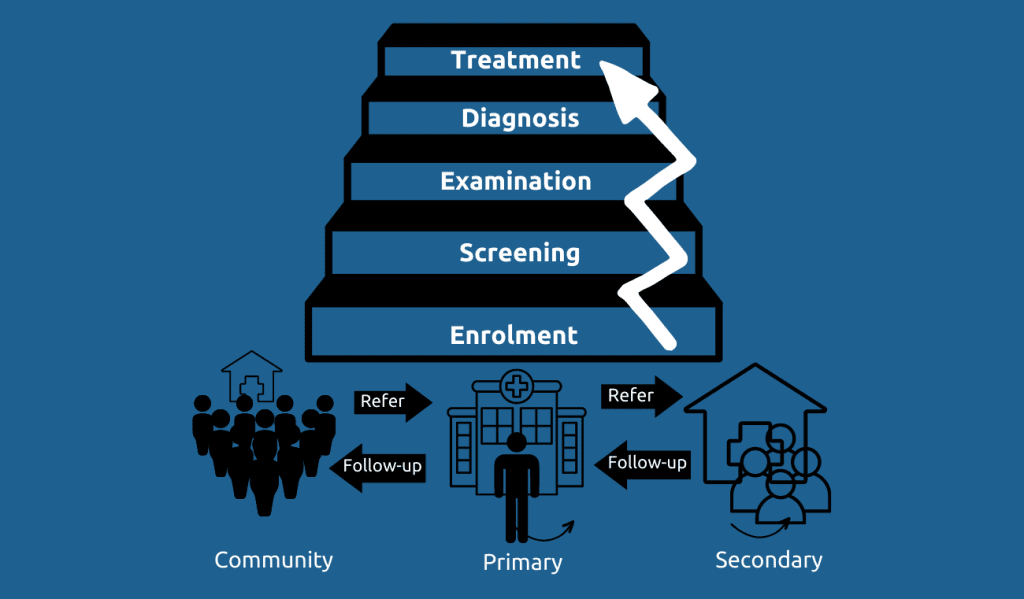
The main goal of the continuum of care is to guarantee that patients comply with their treatment plan. This is the most crucial aspect of the healthcare program since it ensures that patients obtain the full advantages of their treatment. Treatment adherence is critical because it lowers the risk of complications and enhances the probability of a favourable outcome. To attain this objective, technology plays a pivotal role. Healthcare providers can employ technology that we utilize in our daily lives to help enhance patient outcomes. For instance, mobile apps can be utilized to oversee patient adherence, offer reminders for appointments and medication, and furnish instant updates on the patient’s condition.
Another crucial objective of the continuum of care is to enhance the productivity and quality of care that healthcare providers deliver. Healthcare providers like doctors and nurses are frequently overworked, and technology can alleviate some of this burden. For instance, electronic health records (EHRs) can be used to streamline the documentation process and offer real-time access to patient information.
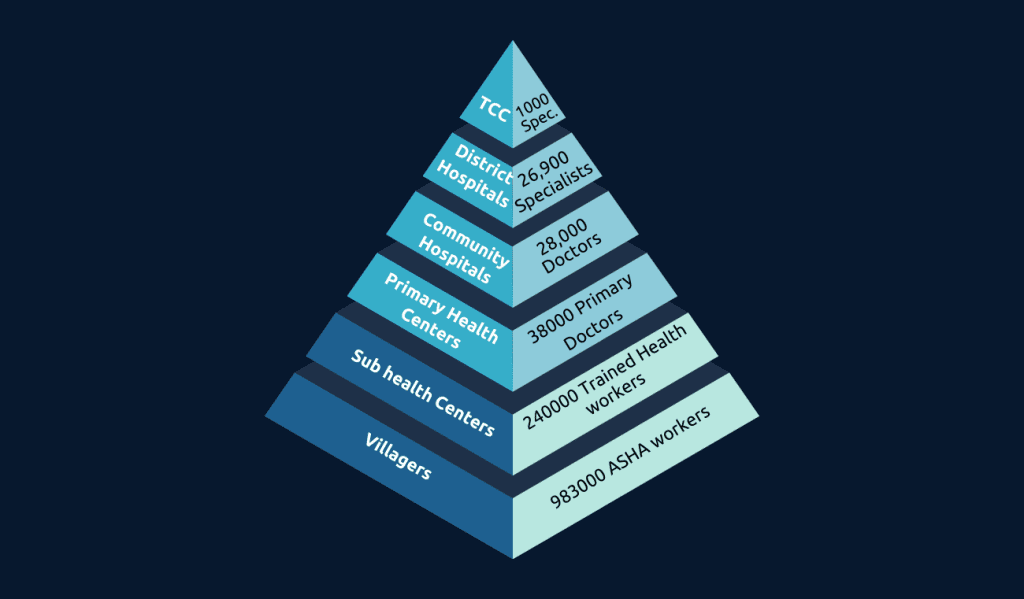
Ultimately, the continuum of care should furnish data to officials and administrators of the program, so that they can make well-informed decisions about the healthcare system. The data should be provided in a user-friendly format so that program officials can rapidly respond to the evolving needs of the program. To overcome the challenges facing the healthcare system, a mobile and tablet app-based system has been developed with several components. The system starts with a community app that conducts population enumeration, assesses the risk of sexually transmitted diseases, screens for non-communicable diseases, and dispenses monthly medications for patients with conditions like hypertension and diabetes. At the healthcare provider level, apps are used for the diagnosis, examination, and management of patients and all information is collected in a central health record accessible to all providers. Finally, program officials and administrators use the system to monitor and respond to the changing needs of the healthcare system, running the technology system at the district and state levels. By ensuring patient adherence to their treatment regimen, improving the productivity and quality of care providers, and providing data to program officials, the healthcare system can be improved. Technology is crucial in achieving these goals and should be utilized to enhance patient outcomes.

India’s healthcare sector faces challenges with transparency and accessibility of information, which is being addressed through a collaborative solution featuring a single market approach and a referral workflow. The system provides real-time information to healthcare providers, ensuring continuity of care and minimizing gaps in treatment. It also tracks patient movement between facilities, reducing the likelihood of patients getting lost in the healthcare system. The healthcare system in India has several benefits, including real-time alerts to ensure patients receive proper care and tracking of unscreened populations. The system provides a comprehensive view for informed decision-making and is designed to solve real-world problems and have a positive impact on society. A notable CSR initiative in Ghana began in 2014 to transcribe medical records with the help of volunteers and without a profit motive. The project focused on engaging health workers and developed through iterative collaboration with Doctor Trust.
The initiative was launched in India by the Prime Minister in 2018 and expanded to five districts by 2019. Despite the setbacks caused by the pandemic in 2020, the system had successfully enrolled 45 billion individuals, and as of January 31, 2021, 135 million people across 33 states and 93 districts had joined the system. The program has also involved the training of over 94,000 individuals by contractors and state governments, demonstrating a significant collaborative effort. The primary lesson learned from this program is that it is not solely a technological solution, but rather a government program that necessitates collaboration among various stakeholders, such as AIDS, NPDR, and ACP. Given the program’s magnitude, it presents significant challenges, but successful implementation is contingent upon partnership and collaboration.
Tata Trust has used a multi-tiered training process called the cascade model of training in its CSR initiatives in Ghana and India, which are collaborative efforts involving multiple players. The development of the “You Can’t Sit and Create” apps for healthcare workers involved agile development and tailoring to the needs of different states. The utilization of dashboards was discovered to be high, highlighting the importance of adapting to user needs. The development team faced a challenge in managing reporting for all 33 states, but they were able to offer appropriate assistance. All of the products are open source, enabling different government departments to integrate and collaborate. The outcome of better interoperability and data sharing can significantly benefit the healthcare sector.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the article highlights the role of technology in addressing public health challenges and promoting human progress. Through collaboration between the government and technology companies, programs such as the National Program for Prevention and Control of Cancer, Diabetes, Cardiovascular Disease, and Stroke in India have been implemented to address public health issues on a large scale. The continuum of care is a critical aspect of healthcare that ensures patients comply with their treatment plans, and technology plays a pivotal role in enhancing patient outcomes, increasing the productivity and quality of care delivered by healthcare providers, and furnishing data to officials and administrators of the program to make well-informed decisions. Despite facing several challenges, India is making progress in improving the delivery of health services through initiatives such as the development of digital suites of apps and platforms, working towards a healthier and more prosperous future for its citizens.
Author
-

Head, Global Social Innovation, Environmental Social and Governance